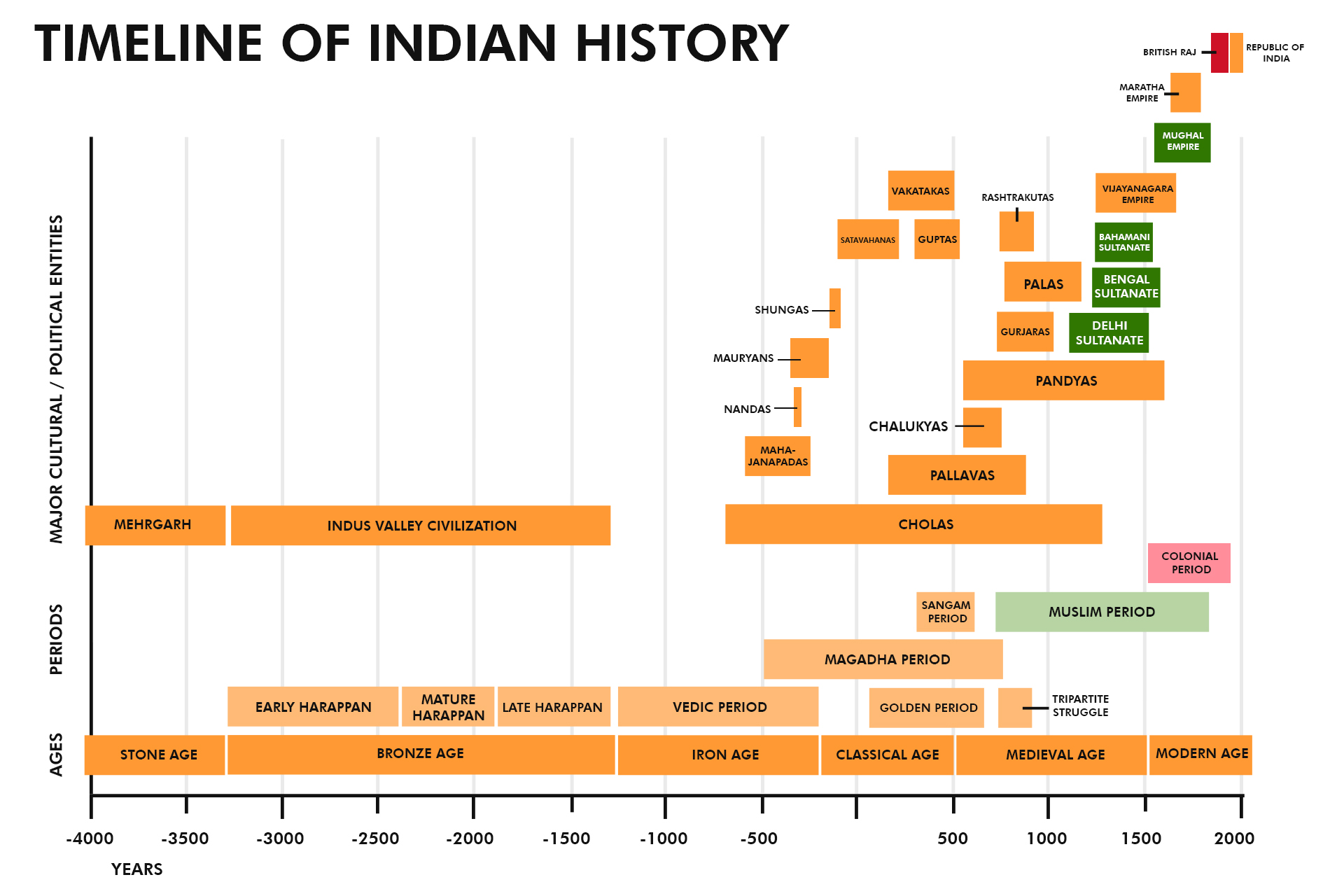
India, a land of rich history and cultural heritage, has seen the rise and fall of numerous dynasties that have left an indelible mark on its timeline. From the mighty Mauryas to the opulent Mughals, the passage of time in India has been defined by the rule of these dynasties. Their reigns have shaped not only the political landscape of the country but also its art, architecture, and socio-cultural fabric. It is fascinating to delve into the chronology of these dynasties and observe how they played a crucial role in shaping India as we know it today.
Explore the rich history of India through its dynasties! Beginning with the Maurya Dynasty in 322 BCE, which was followed by the Gupta Dynasty in the 4th century CE. Next came the Delhi Sultanate, ruling from the 13th to the 16th century, followed by the Mughal Empire from the 16th to the early 18th century. Finally, the British Raj emerged in the mid-18th century and lasted until Indian independence in 1947. These dynasties trace the passage of time and the evolution of India’s cultural, social, and political landscape.
Contents
- The Rise and Fall of Dynasties in India
- The Passage of Time: Continuation of Dynasties in India
- The Unfolding of Dynasties: A Continuation of India’s Rich History
- Dynasties in India in Chronological Order: Tracing the Passage of Time
- Dynasties in India in Chronological Order: Tracing the Passage of Time
- THE HISTORY OF INDIA in 12 Minutes – Part 1
The Rise and Fall of Dynasties in India
India has a rich and diverse history, shaped by the rise and fall of various dynasties that left their mark on the country’s culture, architecture, and social fabric. From ancient times to the present day, dynastic rule has played a crucial role in shaping India’s destiny. Tracing the passage of time, let us delve into the chronological order of the dynasties that have left an indelible impact on India’s history.
The Indus Valley Civilization (3300-1300 BCE)
The Indus Valley Civilization, also known as the Harappan Civilization, was one of the earliest urban civilizations in the world. Flourishing around the Indus River basin, this civilization thrived from 3300 to 1300 BCE. Despite the absence of a clear ruling dynasty, the Indus Valley Civilization had a well-organized system of governance and trading networks.
The cities of Mohenjo-daro and Harappa were the two prominent centers of the Indus Valley Civilization. The society was characterized by well-planned cities, advanced drainage systems, and a script that is yet to be deciphered fully. The decline of the Indus Valley Civilization is still a subject of speculation, with theories ranging from natural disasters to invasion.
The Indus Valley Civilization left behind a rich legacy, evident in its impressive urban planning, advanced agricultural practices, and remarkable craftsmanship. The excavations at Harappa and Mohenjo-daro have provided invaluable insights into the social, economic, and cultural aspects of this ancient civilization.
Notable Features of the Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization boasted several notable features that make it a fascinating subject of study. These include:
- The urban planning and architecture of the cities, with well-laid drainage systems and multi-story buildings.
- The advanced agricultural techniques employed by the civilization, including the use of canals and crop rotation.
- The intricate craftsmanship displayed in various artifacts, such as pottery, jewelry, and seals.
- The existence of a script that baffles historians and archaeologists to this day.
The Indus Valley Civilization provides a unique glimpse into the ancient civilization that laid the foundation for subsequent dynasties in the Indian subcontinent.
Legacy of the Indus Valley Civilization
The legacy of the Indus Valley Civilization can be seen in various aspects of contemporary Indian society. Some of these include:
- The continued practice of agriculture and irrigation systems developed by the Indus Valley Civilization.
- The influence of Indus Valley art and motifs in modern Indian design and architecture.
- The presence of urban centers and well-planned cities in the Indian landscape.
- The cultural and linguistic diversity of India, which can be traced back to the diverse communities in the Indus Valley Civilization.
The Indus Valley Civilization marks the beginning of the chronological order of dynasties in India and provides a fascinating glimpse into the early roots of Indian civilization.
The Maurya Empire (322-185 BCE)
The Maurya Empire, founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, was one of the largest and most powerful empires in ancient India. Spanning over a vast territory, including present-day India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, the Maurya Empire played a pivotal role in shaping the political landscape of the Indian subcontinent.
Under the rule of Emperor Ashoka, the Maurya Empire reached its zenith. Ashoka’s reign is particularly notable for his conversion to Buddhism and his efforts in spreading the principles of peace and non-violence. His inscriptions, known as the Ashokan Edicts, provide valuable insights into the social, political, and religious aspects of the Maurya Empire.
The Maurya Empire declined after Ashoka’s death, with subsequent weak rulers leading to its fragmentation and eventual disintegration. However, the Maurya Empire left a lasting impact on India’s history through their administrative reforms, establishment of a centralized bureaucracy, and promotion of trade and commerce.
Notable Features of the Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire was characterized by several notable features that contributed to its significance:
- A centralized administration with provinces headed by governors appointed by the emperor.
- The establishment of a vast network of roads and highways for efficient governance and trade.
- The dissemination of Buddhism as a state religion, led by Emperor Ashoka.
- The development of a sophisticated coinage system and promotion of trade and commerce.
The Maurya Empire’s impact on governance, infrastructure development, and the spread of Buddhism had a lasting influence on subsequent dynasties in India.
Legacy of the Maurya Empire
The legacy of the Maurya Empire can be observed in various aspects of Indian history and culture. Some of these include:
- The influence of Ashoka’s principles of non-violence and religious tolerance in shaping India’s cultural ethos.
- The Mauryan administrative system, which laid the foundation for subsequent dynasties and governance structures.
- The spread of Buddhism and its integration into Indian society, which continues to be a significant religion in the country.
- The development of trade and infrastructure, which set the stage for subsequent economic growth and urbanization.
The Maurya Empire stands as a significant chapter in India’s history, characterized by political power, cultural achievements, and the spread of ethical principles.
The Gupta Empire (320-550 CE)
The Gupta Empire, often referred to as the “Golden Age” of India, emerged in 320 CE and lasted until 550 CE. Under the rule of Chandragupta I, the Gupta Empire expanded its influence, encompassing large parts of northern India.
The Gupta Dynasty is known for its significant contributions to art, literature, science, and mathematics. The period witnessed a flourishing of Indian culture, with advancements in various fields and the patronage of scholars and artists.
The Gupta Empire’s decline can be attributed to a combination of factors, including invasions by the Huna and the pressure of regional powers. Despite its eventual decline, the Gupta Empire had a profound impact on India’s cultural, scientific, and socio-political landscape.
Notable Features of the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire is known for several notable features that distinguish it from other dynasties:
- The patronage of scholars and artists, leading to advancements in literature, art, and philosophy.
- The development of the decimal system, advanced metallurgical techniques, and the concept of zero in mathematics.
- The reign of Chandragupta II, also known as Chandragupta Vikramaditya, who fostered a golden age of trade and diplomacy.
- The establishment of a centralized administration, with provinces governed by appointed officials.
The Gupta Empire’s contributions in the fields of art, mathematics, and governance continue to shape India’s identity and heritage.
Legacy of the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire’s legacy can be seen in various aspects of Indian culture and society. Some of these include:
- The artistic and literary achievements of the period, which influenced subsequent cultural productions.
- The development of scientific and mathematical concepts that laid the foundation for future advancements.
- The organization of society into a hierarchical structure, which became a template for future social systems.
- The preservation of ancient Indian texts and scriptures.
The Gupta Empire’s contributions to art, science, and governance consolidated its position as a pivotal dynasty in India’s history.
The Mughal Empire (1526-1857)
The Mughal Empire, established by Babur in 1526, marked a significant phase in India’s history. Originating from Central Asia, the Mughals ruled over a vast empire that extended to most of the Indian subcontinent.
The Mughal Empire is known for its rich cultural heritage, including remarkable architectural monuments, exquisite artwork, and a synthesis of Indian and Central Asian traditions. The reigns of emperors such as Akbar, Jahangir, and Shah Jahan are considered the high points of the Mughal Empire.
The decline of the Mughal Empire began with the weakening of central authority, coupled with invasions and regional revolts. The empire faced challenges from various external forces, including the British East India Company, ultimately leading to its downfall in 1857.
Notable Features of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire is distinguished by several notable features that shaped its historical significance:
- The establishment of a centralized administration and a sophisticated system of governance.
- The patronage of art and architecture, resulting in iconic structures such as the Taj Mahal and Red Fort.
- The policy of religious tolerance and the promotion of syncretic cultural practices.
- The introduction of Persian and Central Asian traditions that deeply influenced Indian culture.
The artistic, architectural, and cultural achievements of the Mughal Empire continue to inspire and captivate audiences to this day.
Legacy of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire’s legacy is embedded in various aspects of Indian culture and history. Some of these include:
- The architectural marvels and the exquisite craftsmanship that can be seen in monuments across India.
- The integration of Persian and Central Asian cultural elements into Indian traditions.
- The development of a unique Mughal style of painting known for its intricate details and vibrant colors.
- The legacy of religious tolerance and cultural syncretism that is visible in Indian society.
The Mughal Empire’s contributions to art, architecture, and cultural integration have left an indelible mark on India’s history.
The Passage of Time: Continuation of Dynasties in India
The dynastic history of India extends beyond the four mentioned above. From the Cholas in the south to the Marathas in the west, India has witnessed the rise and fall of numerous dynasties that have shaped its diverse cultural tapestry. Each dynasty played a unique role, leaving behind legacies that range from architectural wonders to artistic marvels, from educational institutions to religious establishments.
The dynastic order in India is a testament to its vibrant and multifaceted history. It is a reminder of the rich heritage that has been passed down through generations, laying the foundation for the India we see today. By tracing the passage of time through these dynasties, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces and factors that have influenced India’s growth and development.
The Unfolding of Dynasties: A Continuation of India’s Rich History
The history of India is intricately woven with the rise and fall of dynasties that have shaped the country’s socio-cultural fabric. From ancient times to the modern era, the chronological order of dynasties in India offers a captivating narrative of power struggles, cultural exchange, architectural brilliance, and socio-political transformations. Let us explore a different dimension of dynasties in India and trace their journeys through time.
The Chola Dynasty (848-1280 CE)
The Chola Dynasty, which emerged in the 9th century CE, marked a golden period in South Indian history. Ruling over the region encompassing present-day Tamil Nadu and parts of Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka, the Cholas were known for their administrative prowess, military might, and patronage of art and literature.
The reign of Rajendra Chola I saw the Chola Empire reach its zenith. He expanded the empire’s territories through successful military campaigns, extending its influence beyond the Indian subcontinent. The Cholas made significant contributions to architecture, with iconic structures like the Brihadeeswarar Temple in Thanjavur standing as testaments to their grandeur.
The decline of the Chola Dynasty can be attributed to a combination of factors, including internal conflicts, invasions from other powers, and the emergence of regional forces. However, the Cholas left an enduring impact on South Indian culture and society through their architectural marvels, administrative systems, and literary works.
Dynasties in India in Chronological Order: Tracing the Passage of Time
In the vast expanse of Indian history, several dynasties have risen and fallen, shaping the cultural, political, and social landscape of the country. Tracing the passage of time, these dynasties provide a glimpse into India’s rich heritage and diverse civilizations.
The Maurya Dynasty, founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, marks the beginning of the imperial rule in India. This powerful dynasty was succeeded by the Gupta Dynasty, known for its golden age of arts, science, and literature. The next significant dynasty was the Mughal Dynasty, which ruled from the 16th to the 19th century and left behind a lasting architectural legacy.
Another crucial dynasty was the Maratha Dynasty, which rose to prominence in the 17th century, challenging the Mughal rule and establishing its dominance in western India. British colonization brought the British Raj, which ruled India from 1858 until independence in 1947.
Additionally, there were several regional dynasties, such as the Chola, Vijayanagara, and Mysore Dynasties in South India, and the Rajput and Sikh Dynasties in the North. These dynasties played a significant role in shaping the regional culture and history of their respective areas.
Dynasties in India in Chronological Order: Tracing the Passage of Time
- 1. The Maurya Dynasty, founded by Chandragupta Maurya, ruled from 322 BCE to 185 BCE.
- 2. The Gupta Dynasty, known for its golden age of art, science, and literature, lasted from 320 CE to 550 CE.
- 3. The Chola Dynasty, famous for its maritime empire and temple architecture, thrived from 850 CE to 1267 CE.
- 4. The Mughal Dynasty, renowned for its architectural wonders like the Taj Mahal, reigned from 1526 CE to 1857 CE.
- 5. The British Raj, which marked British colonial rule in India, lasted from 1858 CE to 1947 CE.
THE HISTORY OF INDIA in 12 Minutes – Part 1