Dynasties have had a profound impact on the government of ancient Egypt, shaping its structure and policies for centuries. One striking example is the continuity of power within a dynasty, with each ruling family exerting control over various aspects of the government. This stability allowed the Egyptian government to develop and flourish, as the rulers passed down their knowledge and experience to successive generations.
An important aspect of how dynasties affected the Egyptian government is the concept of divine kingship. Pharaohs, as the rulers of Egypt, were considered to be gods on earth, serving as intermediaries between the people and the divine. This belief imbued the government with a sense of religious authority and legitimacy, elevating the pharaoh to a position of immense power. The intertwining of religion and government played a crucial role in shaping the policies and decisions of the ruling dynasties.
Dynasties had a profound impact on the Egyptian government. As each dynasty came to power, new rulers brought changes to the political, economic, and social structures of the civilization. They shaped the government to reflect their ideas and priorities. Some dynasties centralized power, while others decentralized it. Dynasties also impacted Egypt’s foreign policy and trade relationships. Overall, dynasties played a crucial role in shaping the Egyptian government throughout history.
Contents
- The Transition of Power: How Dynasties Reshaped Egyptian Government
- Shaping an Empire: Dynastic Influences on Egyptian Government
- In Conclusion
- Impact of Dynasties on Egyptian Government
- Key Takeaways: How Did Dynasties Affect Egyptian Government
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What impact did dynasties have on the political structure of ancient Egypt?
- 2. How did dynasties influence the legal system of ancient Egypt?
- 3. Did dynasties impact the economy of ancient Egypt?
- 4. How did dynasties influence the religious practices of ancient Egypt?
- 5. How did dynasties affect social structure and class divisions in ancient Egypt?
- Ancient Egyptian Government: Interesting (Facts) and History.
The Transition of Power: How Dynasties Reshaped Egyptian Government
Throughout ancient Egyptian history, dynasties played a crucial role in shaping and influencing the government structure of the civilization. These ruling families established a hereditary succession system, where power and authority were passed down from one generation to the next. The impact of dynasties on the Egyptian government was profound, shaping not only the structure of governance but also the religious, social, and economic aspects of the civilization. This article explores the various ways in which dynasties affected the Egyptian government.
1. Consolidation of Power and Centralized Authority
The establishment of a dynasty in ancient Egypt often marked a consolidation of power and the centralization of authority. As a dynasty took control, the pharaoh’s rule became more consolidated, leading to a more centralized government. This centralization allowed for more efficient decision-making and administration of the state, enabling the rulers to implement policies and enforce laws effectively. The pharaoh, as the head of the dynasty, held supreme authority and was regarded as a divine figure, ensuring obedience and loyalty from the people.
Under the centralized rule of the pharaoh, the government apparatus expanded to support the growing administrative needs of the kingdom. The pharaoh appointed officials, such as viziers, scribes, and governors, to manage different administrative divisions of the state. These officials assisted in governing the country, collecting taxes, coordinating construction projects, and overseeing land management. The establishment of a bureaucratic system allowed for the smooth functioning of the government and the implementation of the pharaoh’s policies across the kingdom.
Furthermore, dynasties brought stability to the government by ensuring a clear line of succession. The hereditary nature of the Egyptian dynasties meant that the next ruler was predetermined, reducing the chances of power struggles or succession crises. This stability provided the government with continuity and allowed for long-term planning and development. It also fostered a sense of stability among the people, as they could rely on the established order of governance.
2. Influence on Religious Practices
Ancient Egyptian dynasties also had a significant influence on religious practices and beliefs. The pharaoh, as the divine ruler, played a central role in religious ceremonies and rituals. The concept of Ma’at, which represented the principles of truth, justice, and balance, was interwoven with the authority of the pharaoh and the stability of the dynasty.
The dynastic system reinforced the idea of divine rule, with the pharaohs believed to be the intermediaries between the gods and the people. The religious cults associated with the pharaohs and their divine ancestors were instrumental in legitimizing the authority of the ruling dynasty. Temples were constructed, and elaborate rituals were performed to maintain the harmonious balance between the earthly and divine realms.
Additionally, each dynasty brought its own religious beliefs and traditions, which influenced the state religion. The deities associated with the ruling dynasty gained prominence, and their temples and cults received significant support and resources. The pharaoh often aligned themselves with specific gods, emphasizing their divine connection and strengthening their political legitimacy.
3. Impact on Economic Policies and Trade
Dynasties had a profound impact on the economic policies and trade of ancient Egypt. They played a vital role in the development and management of resources, infrastructure, and trade networks. The pharaohs, as the rulers of the dynasties, implemented policies to promote agriculture, which formed the backbone of the Egyptian economy.
Under the rule of various dynasties, extensive irrigation systems were constructed to support agricultural activities. The pharaohs oversaw projects such as the construction of canals, dams, and reservoirs, ensuring a consistent water supply for farming. This focus on agriculture not only ensured the stability of the food supply but also resulted in surplus production, which could be traded domestically and internationally.
Dynasties also played a crucial role in facilitating trade with neighboring regions and beyond. They established diplomatic and economic relations with other kingdoms, resulting in the exploration of new trade routes and the introduction of exotic goods. The pharaohs encouraged the establishment of ports and trade centers along the Nile River, fostering economic growth and cultural exchange.
a. Development of International Trade Networks
Some dynasties expanded Egypt’s trade networks beyond the immediate region, with notable examples being the New Kingdom dynasties. The pharaohs of the New Kingdom era established diplomatic ties with distant lands such as the Levant, Nubia, and even the ancient empires of Mesopotamia. These connections opened avenues for the exchange of goods, technologies, and ideas, enriching Egyptian society and promoting cultural diversity.
The influx of foreign trade and goods brought about by these relationships had a significant impact on the Egyptian economy, influencing the social hierarchy and contributing to the wealth of the ruling dynasty. The pharaohs encouraged the trade of luxury items, such as gold, incense, precious stones, exotic woods, and rare animal products, which added to their prestige and power.
Moreover, the economic prosperity resulting from these trade networks enabled the pharaohs to fund grand construction projects, such as the building of temples, monuments, and palaces. These architectural achievements served as symbols of power and authority, further strengthening the position of the ruling dynasty.
4. Influence on Arts, Architecture, and Cultural Identity
Dynasties left an indelible mark on the arts, architecture, and cultural identity of ancient Egypt. The pharaohs and their ruling families actively supported and patronized artistic endeavors, resulting in the creation of magnificent artworks, architectural marvels, and cultural innovations.
Ancient Egyptian art flourished under the dynastic rule, with each dynasty contributing its unique artistic style and motifs. The depiction of pharaohs in statues, paintings, and reliefs showcased the idealized portrayals of the royal family, emphasizing their divine status and the cult of personality surrounding them.
Architecture also experienced significant developments under the reign of different dynasties. The construction of monumental structures, such as the pyramids, temples, and tombs, became a hallmark of ancient Egyptian architecture. These structures served religious, governmental, and funerary purposes, reflecting the grandeur and power of the ruling dynasty.
a. The Golden Age of Egyptian Architecture: The New Kingdom Dynasties
The New Kingdom dynasties witnessed a golden age of Egyptian architecture, marked by the construction of iconic structures such as the Temple of Luxor, the Ramesseum, and the mortuary temple of Hatshepsut at Deir el-Bahari. These architectural masterpieces showcased the wealth, prosperity, and artistic achievements of the ruling dynasty.
Furthermore, cultural identity and traditions were deeply intertwined with the ruling dynasties. The pharaohs actively promoted and preserved Egyptian cultural practices and religious rituals. They were responsible for the construction and maintenance of religious monuments, which served as centers for worship and community gatherings.
The royal family, as patrons of the arts, ensured the continuation of cultural traditions through their support of musicians, dancers, and craftsmen. The dynasties played a critical role in preserving and transmitting the cultural heritage of ancient Egypt.
Shaping an Empire: Dynastic Influences on Egyptian Government
Another significant aspect of how dynasties affected Egyptian government is through the expansion of territories and the establishment of an empire. As certain dynasties gained power and influence, they aimed to extend their dominion beyond the borders of Egypt.
The New Kingdom dynasties, particularly the 18th dynasty, witnessed a period of unprecedented expansion. Led by pharaohs like Thutmose III and Ramses II, Egypt’s empire expanded into territories such as Nubia, Canaan, and Syria. The acquisition of these lands brought wealth, resources, and strategic advantages to the Egyptian government.
The expansion of the empire necessitated the establishment of administrative centers and military garrisons in the conquered territories. This led to an increase in the size and complexity of the government apparatus, as the rulers had to govern both the core Egyptian territories and the newly acquired lands. The administrative structure in these regions required coordination with the central government, which further shaped the Egyptian governance system.
Moreover, the empire-building efforts of the dynasties led to the establishment of diplomatic ties and alliances with foreign kingdoms. These diplomatic relationships influenced Egypt’s foreign policy and allowed for cultural exchanges, knowledge transfer, and the spread of Egyptian influence beyond its borders.
1. Integration of Conquered Territories into the Egyptian Government
As dynasties expanded the Egyptian empire, they faced the challenge of integrating the conquered territories into the existing governmental structure. The rulers developed administrative mechanisms to govern these regions, often appointing local elites as governors or administrators under the authority of the central government.
The pharaohs aimed to assimilate the conquered territories by imposing Egyptian cultural practices, religious beliefs, and governmental systems. The administrative centers established in these regions became outposts of Egyptian governance, ensuring the rule of law, tax collection, and the maintenance of social order. The integration of these territories into the Egyptian government provided the ruling dynasties with strategic advantages, access to resources, and increased influence in the region.
Furthermore, the annexation of new territories contributed to the wealth and prestige of the ruling dynasty. The tribute and taxes extracted from these regions bolstered the Egyptian economy and funded grand projects and campaigns. The expansion of the empire under the dynasties enhanced Egypt’s position as a dominant regional power, influencing the geopolitical landscape of the ancient Near East.
2. Military Expansion and Defense Strategy
The military played a crucial role in the expansion of the Egyptian empire under dynastic rule. Pharaohs invested in building military infrastructure, equipping armies, and organizing military campaigns to secure and defend their territories.
Dynasties established military hierarchies and structures, with the pharaoh as the supreme commander of the armed forces. The ruling families supported the military by providing resources, land, and manpower. The military elite, led by skilled generals and commanders, played a significant role in ensuring the success of military campaigns and the consolidation of power.
As the empire expanded, the defense strategy of the Egyptian government underwent modifications. The ruling dynasties built fortresses, fortified cities, and military outposts in strategic locations to secure the borders and protect the empire from external threats.
3. Impact on Foreign Relations and Diplomacy
The expansion of the Egyptian empire under dynastic rule significantly influenced foreign relations and diplomacy. The pharaohs engaged in diplomatic efforts to maintain peace, secure alliances, and expand trade networks.
Through diplomatic marriages, the ruling dynasties established alliances with powerful kingdoms, ensuring stability and security along the borders. These alliances provided strategic advantages, as they deterred potential invaders and allowed for mutual economic and political benefits.
Moreover, dynastic rule led to the establishment of diplomatic contacts and diplomatic missions with neighboring kingdoms. The ancient Egyptians sought to maintain peaceful relations and forge trade agreements, often mediated through diplomatic envoys and emissaries.
In Conclusion
The influence of dynasties on the Egyptian government was multi-faceted and far-reaching. They consolidated power, centralized authority, and ensured a clear line of succession, providing stability and continuity. Dynasties influenced religious practices, economic policies, and trade networks, shaping the cultural identity of ancient Egypt. The expansion of territories and establishment of an empire under dynastic rule further transformed the Egyptian government, necessitating the integration of conquered territories, military expansion, and the establishment of diplomatic ties. Through these various mechanisms, dynasties played a pivotal role in shaping and reshaping the governance structure of ancient Egypt.
Impact of Dynasties on Egyptian Government
Dynasties in ancient Egypt had a profound influence on the government structure and organization. The succession of dynasties played a crucial role in shaping the political landscape of the civilization.
One of the notable impacts of dynasties was the establishment of hereditary rule, where power and authority were passed down from one generation to another within a ruling family. This led to stability and continuity in the governance of ancient Egypt.
The pharaoh, as the head of the ruling dynasty, held absolute power and was considered a divine figure. The dynastic system emphasized the importance of maintaining order and balance in society. The pharaoh’s role extended beyond political leadership and encompassed religious and administrative responsibilities.
Dynasties also influenced the hierarchy of government officials. Members of the ruling family were often given top positions, such as viziers or high priests, ensuring their authority and control over various aspects of governance.
Key Takeaways: How Did Dynasties Affect Egyptian Government
- The rule of dynasties in Ancient Egypt led to a centralized government.
- Pharaohs were considered divine rulers and had absolute power in the government.
- Dynasties brought stability to the government and were responsible for building monumental structures.
- Succession within dynasties created a smooth transition of power.
- The pharaoh’s role as a political, religious, and military leader shaped Egyptian society.
Frequently Asked Questions
Dynasties played a significant role in shaping the government of ancient Egypt. Here are some frequently asked questions about how dynasties affected the Egyptian government.
1. What impact did dynasties have on the political structure of ancient Egypt?
Dynasties in ancient Egypt had a profound impact on the political structure of the country. Each dynasty was led by a pharaoh who held absolute power and control over the government. The pharaoh was considered a divine ruler and acted as both a political and religious figure. The dynasties established the hereditary monarchy system in Egypt, where power was passed down from one generation to another within the same family. This stability in leadership provided continuity and centralized control over the government.
Moreover, the pharaohs appointed high-ranking officials, such as viziers and governors, to assist in governing different regions of Egypt. These officials were responsible for managing administrative tasks, collecting taxes, and enforcing the pharaoh’s orders. The dynasties created a hierarchical structure within the government, ensuring efficient governance and implementation of policies throughout the kingdom.
2. How did dynasties influence the legal system of ancient Egypt?
Dynasties had a significant influence on the legal system of ancient Egypt. The pharaoh, as the ultimate authority, established laws and regulations that governed the society. These laws were codified and enforced throughout the kingdom. The dynasties were responsible for ensuring the stability and consistency of the legal system.
The pharaoh appointed judges and scribes who interpreted and administered the laws. These judges were responsible for resolving disputes, maintaining order, and delivering justice. The dynasties introduced the concept of ma’at, which emphasized harmony, truth, and justice. The legal system of ancient Egypt aimed to uphold these principles and promote social order.
3. Did dynasties impact the economy of ancient Egypt?
Dynasties had a significant impact on the economy of ancient Egypt. The pharaohs controlled and regulated economic activities, such as agriculture, trade, and taxation. The dynasties implemented policies to ensure the prosperity and stability of the economy.
Under the dynasties, agricultural production and irrigation systems flourished. This led to surplus food production, which supported the growing population and provided resources for trade. The pharaohs also maintained control over valuable resources, such as gold, copper, and precious stones, which contributed to the wealth and economic power of Egypt.
4. How did dynasties influence the religious practices of ancient Egypt?
Dynasties had a profound influence on the religious practices of ancient Egypt. The pharaoh, as the divine ruler, played a central role in religious ceremonies and rituals. The dynasties promoted the worship of specific deities and built temples and monuments dedicated to these gods and goddesses.
The dynasties also ensured the continuity of religious traditions. They appointed high priests and priestesses who performed important religious rites and maintained the temples. The pharaohs themselves were considered to be divine, and their rule was seen as a manifestation of the gods’ will. The dynasties created a close relationship between the government and religious institutions, reinforcing the authority and power of the pharaoh.
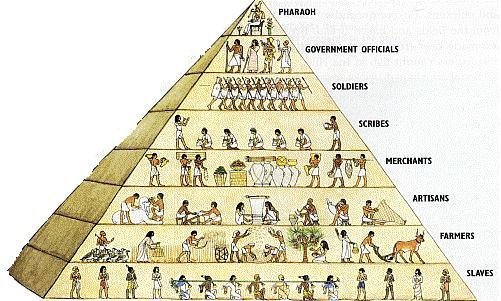
Dynasties had a significant impact on the social structure and class divisions in ancient Egypt. The pharaoh and the ruling elite occupied the highest social class. They held immense wealth, land, and power. The nobility and high-ranking officials were also part of the upper class.
On the other hand, the majority of the population belonged to the lower social class, which included farmers, laborers, and artisans. The dynasties maintained a social hierarchy, where each class had specific roles and responsibilities. The pharaohs ensured the stability of this social structure, which maintained order and facilitated the efficient functioning of society.
Ancient Egyptian Government: Interesting (Facts) and History.
In conclusion, dynasties played a crucial role in shaping and influencing the Egyptian government throughout its history. They provided stability and continuity by establishing a hereditary system of rulership, ensuring the smooth succession of power from one generation to the next.
Moreover, the Pharaohs of ancient Egypt held absolute authority and were considered divine rulers, which allowed them to centralize political and religious power. This centralized control allowed the Egyptian government to efficiently oversee projects such as monumental construction, economic development, and the administration of justice.