Ancient Egypt, known for its awe-inspiring pyramids and vast desert landscapes, also holds a rich history filled with numerous dynasties. These dynasties, spanning over thousands of years, shaped the civilization of ancient Egypt in profound ways. From the rise and fall of powerful pharaohs to the advancements in art, architecture, and engineering, the dynasties of ancient Egypt offer a fascinating glimpse into the past.
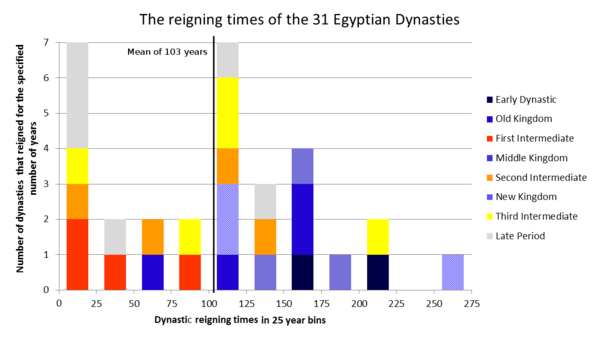
In total, there were approximately 31 dynasties in ancient Egypt. Each dynasty was led by a succession of pharaohs who ruled over the kingdom. These ruling families brought stability, prosperity, and at times, conflict and upheaval to the land. One of the most remarkable aspects of ancient Egyptian dynasties is their longevity. Some dynasties lasted for several centuries, leaving a lasting impact on the culture, religion, and governance of the empire. Through the study of these dynasties, we gain insights into the complex and enduring civilization that shaped one of the greatest ancient civilizations in history.
Ancient Egypt had a total of 31 dynasties throughout its rich history. The dynasties spanned over a period of approximately 3000 years, starting with the Early Dynastic Period around 3100 BCE and ending with the Late Period around 332 BCE. Each dynasty represented a line of kings or rulers, and they played a significant role in shaping Egypt’s political, cultural, and religious landscape. The pyramids, temples, and other architectural wonders that still stand today are a testament to the enduring legacy of ancient Egypt’s dynasties.
Contents
The Complexity of Ancient Egyptian Dynasties
Ancient Egypt, with its rich and fascinating history, is renowned for its dynastic rule. The concept of dynasties in ancient Egypt refers to a succession of rulers from the same family, who held power over the land for a substantial period. However, understanding the exact number of dynasties in ancient Egypt can be quite complex. The classification of dynasties depends on various factors, including political, cultural, and historical aspects.
The Beginning of Ancient Egyptian Dynasties
The earliest recognized Egyptian dynasty, commonly known as the Early Dynastic Period, emerged around 3100 BCE, following the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under King Menes, also known as Narmer. This marked the beginning of centralized political control and the establishment of the first dynasty of ancient Egypt. The length and specific number of dynasties that followed this initial period are subject to ongoing scholarly debate and interpretation.
The early dynasties were characterized by both political and cultural changes as the kings consolidated their power and asserted their authority. The capital city shifted, and different regions of Egypt witnessed the rise and fall of various dynasties. The ruling dynasties were typically based in northern Egypt, with the city of Memphis serving as a prominent political and administrative center. However, some dynasties originated from other regions, such as Thebes during the Middle Kingdom.
Through the Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, and New Kingdom periods, the dynastic rule continued, although the political landscape underwent significant transformations. The power and influence of the pharaohs fluctuated, and various dynasties rose and fell during these periods, each leaving behind its mark on Egyptian history and culture.
Challenges in Determining the Exact Number of Dynasties
Determining the precise number of dynasties in ancient Egypt is no easy task. Different sources and scholars have varying interpretations and classifications. One of the reasons for this complexity is the existence of overlapping dynasties and the division of certain periods into separate dynasties due to distinctive ruling families or political changes.
Another challenge stems from the presence of short-lived or “ephemeral” dynasties, which did not have a significant impact on Egyptian history or endure for long periods. Some of these were considered usurpers or ruling families that emerged during periods of political instability or transitional phases.
Moreover, the documentation and preservation of ancient Egyptian history have its limitations. Many original records and monuments have been lost or destroyed over time, making it challenging to reconstruct an accurate timeline of dynastic rule. As a result, historians rely on fragmented evidence, such as inscriptions, tomb paintings, and archival texts, to piece together the chronology of ancient Egyptian dynasties.
Despite these challenges, scholars have categorized ancient Egyptian history into a system of approximately 30 dynasties, known as the “Dynastic Periods.” These periods serve as a useful framework for understanding the continuity and changes in ancient Egyptian society and culture throughout its long history.
Prominent Dynasties of Ancient Egypt
Within the complex web of ancient Egyptian dynasties, several stand out as particularly influential and significant in shaping the nation’s history and culture:
- The Old Kingdom (Dynasties 3-6)
- The Middle Kingdom (Dynasties 11-13)
- The New Kingdom (Dynasties 18-20)
These dynasties represent distinct periods of ancient Egyptian history characterized by notable achievements in art, architecture, politics, and international relations.
The Old Kingdom
The Old Kingdom, spanning from around 2686 to 2181 BCE, saw the construction of iconic structures like the Pyramids of Giza. These dynasties established the centralized power of the pharaoh, developed elaborate burial customs, and implemented a highly organized bureaucracy to govern the empire.
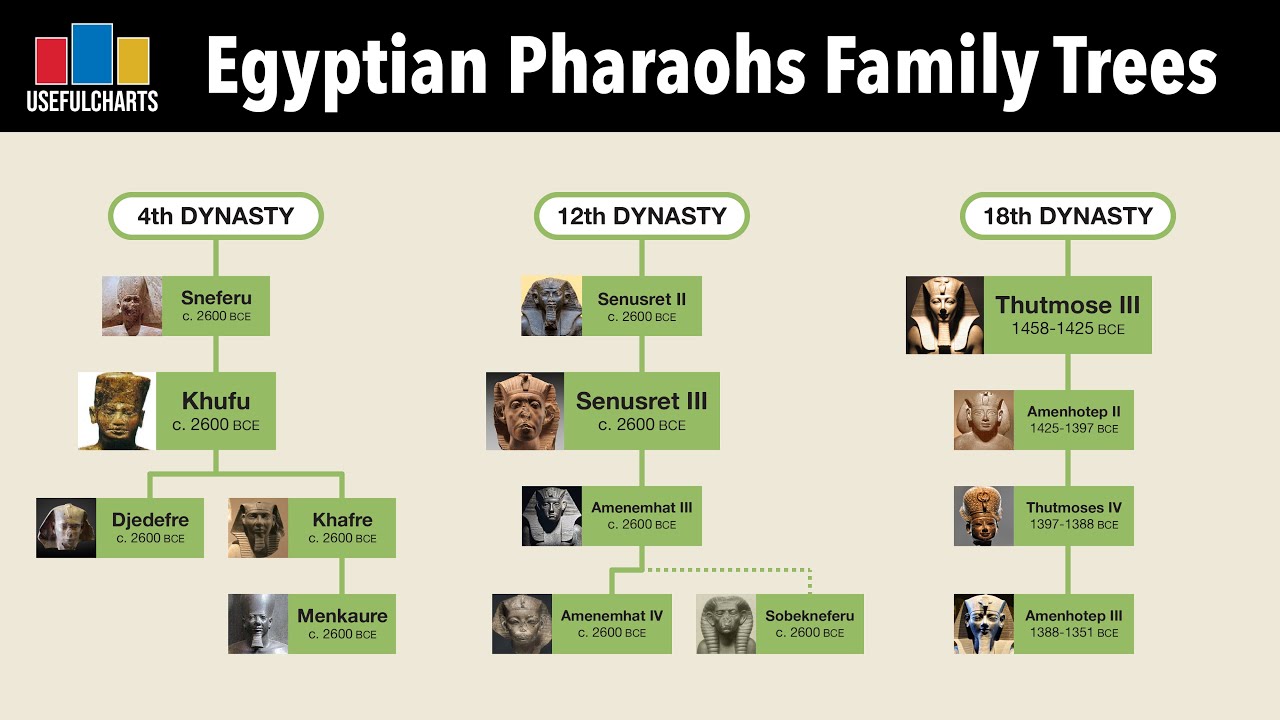
The Fourth Dynasty, in particular, under the famous pharaohs such as Khufu (Cheops), Khafre, and Menkaure, witnessed monumental architectural achievements and the construction of the Great Sphinx and the Great Pyramid. The Old Kingdom laid the foundation for ancient Egyptian civilization and exemplified the height of dynastic power.
The decline of the Old Kingdom was marked by political instability, weak rulers, and economic struggles, leading to the fragmentation of power and the emergence of regional rulers.
The Middle Kingdom
The Middle Kingdom, covering the period from around 2055 to 1650 BCE, witnessed a revival of centralized political control and a return to stability under the rulers of the Twelfth Dynasty. This era saw the pharaohs as more benevolent and actively involved in projects aimed at improving the lives of their subjects.
The Middle Kingdom marked a significant cultural and artistic renaissance, with advancements in literature, poetry, and storytelling. It was during this period that Thebes emerged as a primary center of power, challenging the authority of the traditional Memphis-based ruling elite.
However, as the Middle Kingdom waned, it faced internal conflicts, foreign invasions, and the invasion of the Hyksos, a foreign Semitic people who eventually overthrew the ruling dynasty and established their own in Egypt.
The New Kingdom
The New Kingdom, spanning from approximately 1550 to 1070 BCE, is considered a period of immense power and prosperity for ancient Egypt. This era witnessed monumental military expeditions, territorial expansion, and international diplomacy.
Under the pharaohs of the Eighteenth Dynasty, including prominent rulers such as Hatshepsut, Thutmose III, and Amenhotep III, Egypt reached its peak as a dominant force in the ancient Near East. The New Kingdom also saw religious and artistic developments, including the worship of the god Aten during the reign of Akhenaten.
However, the New Kingdom subsequently faced external threats, particularly from the Sea Peoples and the Libyans, which weakened its influence and led to the decline of dynastic rule.
The Complexity of Ancient Egyptian Dynasties
One aspect of ancient Egypt that continues to captivate historians and enthusiasts alike is the intricate web of dynastic rule. The concept of dynasties in ancient Egypt refers to the reign of rulers from the same family, who held power for a considerable period. However, determining the exact number of dynasties in ancient Egypt is a complex task, encompassing various factors and interpretations.
Factors Influencing the Classification of Dynasties
Several factors contribute to the challenges in determining the precise number of dynasties in ancient Egypt:
- Political changes and power shifts
- Overlapping and ephemeral dynasties
- Loss of historical records and monuments
The shifting political landscape and changes in power dynamics among different regions of Egypt led to the rise and fall of numerous dynasties throughout its history. Additionally, overlapping dynasties and short-lived ruling families make it difficult to establish a clear-cut classification.
The preservation of ancient Egyptian history also presents challenges. Many original records and monuments have been lost or destroyed, making it challenging to reconstruct an accurate timeline of dynastic rule. Consequently, historians must rely on fragmented evidence and inscriptions found in tombs and archaeological sites to piece together the chronology of dynasties.
Prominent Dynasties of Ancient Egypt
Despite the complexities surrounding the classification of dynasties, several periods stand out as significant in ancient Egyptian history:
- The First Dynasty (c. 3100-2890 BCE)
- The Twelfth Dynasty (c. 1985-1795 BCE)
- The Eighteenth Dynasty (c. 1550-1292 BCE)
These dynasties symbolize crucial turning points in ancient Egypt, characterized by political stability, cultural advancements, and territorial expansion.
Ancient Egyptian Dynasties: A Fascinating Tapestry
The study of ancient Egyptian dynasties is a fascinating journey through time. Each dynasty leaves behind a unique imprint on Egyptian history and culture, contributing to the nation’s identity and legacy. Understanding ancient Egyptian dynasties allows us to appreciate the incredible achievements and accomplishments of this ancient civilization that continues to captivate us to this day.
Dynasties in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was ruled by numerous dynasties throughout its rich history. These dynasties were long-lasting ruling families that held power and control over the land and its people. The exact number of dynasties in Ancient Egypt is a subject of debate among historians. However, it is generally accepted that there were approximately 31 dynasties.
The first royal dynasty, known as the Early Dynastic Period, began in 3100 BC with the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt. This marked the beginning of the Old Kingdom, which lasted until 2181 BC. Subsequent dynasties came and went, each leaving their mark on Egyptian history and culture.
One of the most famous dynasties is the 18th dynasty, which saw the reign of influential pharaohs such as Hatshepsut, Akhenaten, and Tutankhamun. This period is often referred to as the New Kingdom and is known for its monumental architecture and military conquests.
Each dynasty had its own unique characteristics and contributed to the overall development and legacy of Ancient Egypt. From the construction of the pyramids to the establishment of religious rituals, these dynasties played a crucial role in shaping the civilization of Ancient Egypt.
Key Takeaways – How Many Dynasties in Ancient Egypt
- Ancient Egypt had 31 dynasties throughout its long history.
- Each dynasty represents a period of time when the ruling family held power.
- The first dynasty of Ancient Egypt began around 3100 BCE.
- The final dynasty, the 31st, ended in 332 BCE with the conquest of Egypt by Alexander the Great.
- The dynasties were ruled by pharaohs, who were considered divine rulers by the Egyptians.
Frequently Asked Questions
In Ancient Egypt, there were numerous dynasties that ruled over the land for thousands of years. These dynasties played a crucial role in shaping the country and its rich history. Here are some frequently asked questions about the dynasties of Ancient Egypt.
1. How many dynasties were there in Ancient Egypt?
Ancient Egypt had a total of 31 dynasties. These dynasties spanned from approximately 3100 BCE to 332 BCE, covering a period of over 3,000 years. Each dynasty marked the reign of a single pharaoh or a line of pharaohs from the same family.
These dynasties are divided into three main periods: the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, and the New Kingdom. Each period had its own unique characteristics and saw the rise and fall of different pharaohs and dynasties.
2. Who was the first pharaoh of Ancient Egypt?
The first pharaoh of Ancient Egypt was Narmer, also known as Menes. He was believed to be the ruler who unified Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt around 3100 BCE, thus establishing the first dynasty and the beginning of Ancient Egyptian civilization.
Narmer was a powerful and influential leader who laid the foundation for the long line of pharaohs that followed him. His rule marked the beginning of a centralized government and the development of a complex hierarchical society in Ancient Egypt.
3. Which dynasty built the Great Pyramids of Giza?
The Great Pyramids of Giza, one of the most iconic symbols of Ancient Egypt, were built during the Old Kingdom period. It was the Fourth Dynasty that was responsible for the construction of these magnificent structures.
Pharaohs such as Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure, who ruled during the Fourth Dynasty, commissioned the construction of these pyramids as elaborate tombs for themselves. The pyramids were built with meticulous precision and served as a testament to the power and wealth of the pharaohs.
4. Which dynasty was known for female pharaohs?
The Eighteenth Dynasty of Ancient Egypt was known for its remarkable female pharaohs. This period marked the rise of powerful queens who took on the role of pharaoh and ruled over Egypt.
One of the most famous female pharaohs from this dynasty was Hatshepsut. She not only served as a queen but also declared herself pharaoh, wearing traditional pharaoh attire and taking on all the roles and responsibilities of a male ruler. Hatshepsut’s reign was filled with prosperity and advancements in arts, architecture, and trade.
5. How did the last dynasty of Ancient Egypt come to an end?
The last dynasty of Ancient Egypt was the Thirtieth Dynasty. This dynasty came to an end with the conquest of Egypt by Alexander the Great in 332 BCE. Alexander’s invasion marked the beginning of the Hellenistic period in Egypt, where Greek influence and culture started to reshape the country.
After Alexander’s death, Egypt fell under the rule of various other dynasties, such as the Ptolemaic Dynasty and the Roman Empire. Although Ancient Egyptian dynasties had come to an end, their legacy can still be seen and admired in the country’s rich history and iconic monuments.
Egyptian Pharaohs Family Tree | Dynasties 1 to 31
In conclusion, Ancient Egypt had a total of 31 dynasties that spanned over thousands of years. These dynasties were ruling families that governed Egypt and shaped its history.
The dynasties of Ancient Egypt were marked by significant achievements in the fields of architecture, art, religion, and governance. Each dynasty had its own unique characteristics and contributions, making Ancient Egypt a fascinating and influential civilization in human history.