Welcome to Navigating the Ancient Egyptian Dynasties Timeline: A Journey Through Millennia, where we uncover the fascinating history of ancient Egypt’s ruling dynasties. Did you know that the ancient Egyptian civilization lasted for over 3,000 years? From the reign of Narmer, the first pharaoh of the First Dynasty, to the rule of Cleopatra, the last pharaoh of the Ptolemaic Dynasty, this timeline takes us on an exploration of the dynasties that shaped one of the world’s most iconic civilizations.
This engaging timeline provides a comprehensive view of the rise and fall of each dynasty, offering valuable insights into the political, cultural, and artistic developments that marked each era. With over 30 dynasties and countless pharaohs to navigate through, this journey through millennia allows us to understand the ebb and flow of power, the religious beliefs, and the monumental achievements of ancient Egypt. Whether you are a history enthusiast, a student, or simply curious about this ancient civilization, this timeline offers a rich and informative experience that transports you back in time.
Explore the rich tapestry of ancient Egyptian dynasties with our comprehensive timeline. Follow the footsteps of pharaohs, from the Old Kingdom to the New Kingdom and beyond. Discover the rise and fall of powerful rulers, iconic monuments, and cultural achievements spanning millennia. Navigating the ancient Egyptian dynasties timeline is an exciting journey through history, revealing the enduring legacy of one of the world’s greatest civilizations.

Contents
- Ancient Egyptian Dynasties Timeline: Unraveling Millennia of History
- Navigating the Ancient Egyptian Dynasties Timeline: A Journey Through Millennia
- Navigating the Ancient Egyptian Dynasties Timeline: A Journey Through Millennia – Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Discover the Secrets of Ancient Egypt | Engineering an Empire | Full Episode | History
Ancient Egyptian Dynasties Timeline: Unraveling Millennia of History
The ancient Egyptian civilization is renowned for its rich culture, monumental architecture, and enigmatic history. Navigating the Ancient Egyptian Dynasties Timeline allows us to embark on a captivating journey through millennia, uncovering the rise and fall of powerful pharaohs, monumental achievements, and significant events that shaped one of the most fascinating civilizations in human history. While exploring this timeline, we can understand the dynastic periods, the prominent pharaohs, and the cultural, political, and religious developments that defined Ancient Egypt’s legacy.
Pre-Dynastic Period (c. 5500-3100 BCE)
The Pre-Dynastic Period marks the early stages of civilization in ancient Egypt, spanning from approximately 5500 BCE to 3100 BCE. This period predates the emergence of centralized government and the formation of dynastic rule. It is characterized by the development of agriculture, the establishment of settlements along the Nile River, and the gradual formation of social structures.
During the Pre-Dynastic Period, Egypt was divided into separate regions known as nomes, each with its own local ruler or chieftain. These nomes often engaged in conflicts and rivalries, leading to the emergence of regional powers. The cultivation of crops such as wheat and barley became central to the economy, and advancements in pottery and craftsmanship were evident.
Archaeological evidence from this period includes intricate pottery designs, early examples of hieroglyphic writing, and burial sites offering insights into religious and funerary rituals. The most notable archaeological finds from the Pre-Dynastic Period include the Narmer Palette, which depicts the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the pharaoh Narmer, symbolizing the beginning of the dynastic era.
Key Highlights of the Pre-Dynastic Period:
- The emergence of settled communities along the Nile River
- Growth of agriculture and domestication of animals
- Development of social structures and regional powers
- Burial practices reflecting religious and funerary rituals
Old Kingdom (c. 2686-2181 BCE)
The Old Kingdom is often referred to as the “Age of the Pyramids” due to the construction of the iconic pyramids at Giza. It spans from approximately 2686 BCE to 2181 BCE and is considered the pinnacle of pharaonic power and centralized administration in ancient Egypt.
Under the Old Kingdom, pharaohs held immense control over the economy, military, and religious institutions. The construction of pyramids as tombs for pharaohs became a symbol of their divine authority and power. Notable pharaohs of this era include Djoser, the ruler associated with the iconic Step Pyramid at Saqqara, and Khufu, who commissioned the Great Pyramid of Giza.
During the Old Kingdom, the administrative system of Egypt was highly centralized, with pharaohs appointing officials known as viziers to oversee governance and manage resources. The society was structured hierarchically, with the pharaoh at the top, followed by the nobles, priests, and common people. The belief in an afterlife and the concept of ma’at (cosmic balance) played significant roles in the religious and social fabric of ancient Egypt.
Key Highlights of the Old Kingdom:
- Construction of iconic pyramids at Giza
- Centralized administration and pharaonic control
- Development of an intricate religious and social hierarchy
- Flourishing art and architectural advancements
Middle Kingdom (c. 2055-1650 BCE)
The Middle Kingdom is often regarded as a period of reunification and restoration after a period of fragmentation known as the First Intermediate Period. It lasted from approximately 2055 BCE to 1650 BCE and witnessed significant political, cultural, and economic transformations.
During the Middle Kingdom, pharaohs aimed to restore stability and unity to Egypt. They focused on infrastructure development, including the construction of irrigation systems, temples, and fortresses. The pharaohs also implemented social reforms to alleviate the hardships faced by common people during the previous period.
One of the most notable pharaohs of the Middle Kingdom is Amenemhat I, who initiated the Twelfth Dynasty and introduced various economic and administrative reforms. The arts flourished during this period, with realistic portrayals of individuals and narratives becoming common in sculptures and tomb paintings.
Key Highlights of the Middle Kingdom:
- Restoration of political stability and reunification of Egypt
- Infrastructure development and social reforms
- Flourishing arts and realistic portrayals in art
- Peaceful trade and diplomatic relations with neighboring regions
New Kingdom (c. 1550-1069 BCE)
The New Kingdom is widely regarded as the most powerful and prosperous period in ancient Egyptian history. It spanned from approximately 1550 BCE to 1069 BCE and witnessed significant military conquests, monumental construction projects, and the expansion of Egyptian influence throughout the Near East.
Pharaohs of the New Kingdom sought to solidify Egypt’s position as a dominant force, engaging in military campaigns to expand its borders and protect its wealth. One of the most prominent pharaohs of this era is Thutmose III, renowned for his military campaigns and cultural patronage. Hatshepsut, the first female pharaoh, also left a lasting legacy through her impressive architectural projects and trade expeditions.
The New Kingdom is known for its grand structures such as the temples of Karnak and Luxor, the mortuary temple of Hatshepsut at Deir el-Bahari, and the Valley of the Kings, where many pharaohs were buried. The period also witnessed the radical shift from polytheism to monotheism during the reign of Akhenaten, who introduced the worship of the sun-disk deity Aten.
Key Highlights of the New Kingdom:
- Military conquests and expansion of Egyptian influence
- Construction of grand temples and mortuary complexes
- Cultural and religious shifts, including the brief period of monotheism
- The reign of iconic pharaohs such as Thutmose III and Hatshepsut
As we navigate the Ancient Egyptian Dynasties Timeline, it becomes evident that the civilization’s rich history is marked by remarkable achievements, political dynamics, and cultural transformations. From the Pre-Dynastic Period to the New Kingdom, each era contributes to our understanding of Ancient Egypt’s legacy, inspiring awe and admiration for a civilization that wielded immense power, technical prowess, and a profound reverence for the divine.
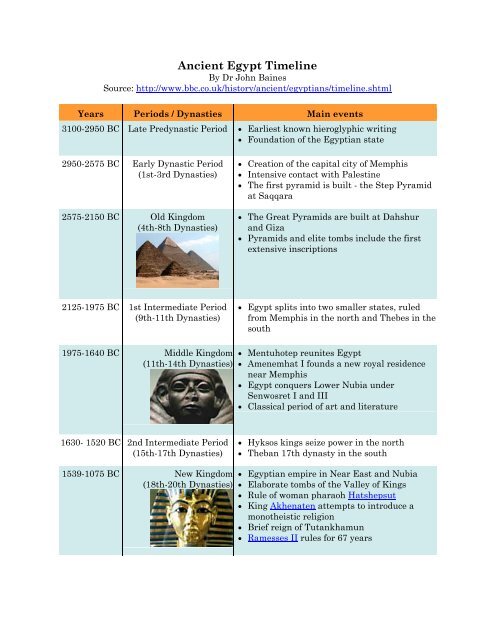
Understanding the ancient Egyptian dynasties timeline is like embarking on a captivating journey through millennia. The timeline spans over 3,000 years and is divided into 31 dynasties, each with its unique rulers, events, and cultural developments.
Navigating this timeline allows us to explore the fascinating rise and fall of powerful pharaohs, the construction of awe-inspiring pyramids, and the flourishing of art, religion, and architecture in ancient Egypt. It provides valuable insights into the civilization’s political, social, and economic transformations.
Starting with the Early Dynastic period around 3100 BCE, we witness the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under Pharaoh Menes, initiating the Old Kingdom, known for the construction of iconic pyramids at Giza. The timeline then traverses through periods of instability, such as the First Intermediate Period, until the Middle Kingdom brings a new era of prosperity and cultural advancements.
The New Kingdom showcases the height of Egyptian power, with influential pharaohs like Hatshepsut, Akhenaten, and Tutankhamun, and the creation of grandiose temples like Karnak and Luxor. The timeline eventually leads us to the Late Period and the conquest of Egypt by foreign powers, including the Persians, Greeks, and Romans.
Exploring the ancient Egyptian dynasties timeline opens a window to a civilization that continues to captivate our imagination and influence modern culture. It allows us to grasp the significance of Egypt’s contributions to art, architecture, religion, and governance, while also appreciating the complexities of its historical narrative.
- Ancient Egyptian history is divided into 31 dynasties that spanned over 3,000 years.
- The Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, and New Kingdom were the major periods of Ancient Egypt.
- The Great Pyramids of Giza were built during the Old Kingdom period.
- Ramses II, also known as Ramses the Great, was one of the most powerful pharaohs in Ancient Egypt.
- The reign of Cleopatra marked the end of the Egyptian dynastic rule.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about navigating the ancient Egyptian dynasties timeline:
1. How many dynasties were there in ancient Egypt?
Ancient Egypt was divided into 31 dynasties, each ruling for a specific period of time. These dynasties spanned over thousands of years, providing a rich and complex history of the region.
The first dynasty began around 3100 BCE and the last one ended around 343 BCE, with the conquest of Egypt by Alexander the Great. These dynasties saw the rise and fall of powerful pharaohs and witnessed major events in Egyptian history.
Navigating the ancient Egyptian dynasties timeline can be a complex task, but there are several resources available to help you. One way is to consult historical books and academic sources that provide detailed information about each dynasty and its rulers.
You can also visit museums and archaeological sites that showcase artifacts and exhibits related to the different dynasties. Online resources, such as interactive timelines and educational websites, can also guide you through the timeline and provide additional information.
3. What were the major dynasties in ancient Egypt?
Several dynasties left a significant impact on ancient Egyptian history. Some of the major dynasties include the Old Kingdom dynasties (Dynasties 3 to 6), which witnessed the construction of iconic pyramids, and the New Kingdom dynasties (Dynasties 18 to 20), known for their powerful pharaohs like Hatshepsut and Tutankhamun.
Other notable dynasties include the Middle Kingdom dynasties (Dynasties 11 to 14), which saw the reunification of Egypt after a period of political and social unrest, and the Late Period dynasties (Dynasties 25 to 31), marked by foreign invasions and struggles for power.
4. What were the main achievements of the ancient Egyptian dynasties?
The ancient Egyptian dynasties achieved many notable achievements that still influence the world today. One of the most remarkable achievements was the construction of monumental structures, including the pyramids of Giza and the temples of Karnak and Luxor.
The dynasties also made significant contributions in the fields of art, literature, and science. They developed a system of writing known as hieroglyphics, created remarkable works of art, and made advancements in medicine and astronomy.
5. What led to the decline of the ancient Egyptian dynasties?
There were several factors that led to the decline of the ancient Egyptian dynasties. One major factor was external invasions, such as the Persian and Assyrian conquests, which weakened the power of the pharaohs and disrupted the stability of the dynasties.
Internal conflicts and political struggles among different factions also contributed to the decline. Economic challenges, such as crop failures and food shortages, further weakened the dynasties and led to social unrest.
Discover the Secrets of Ancient Egypt | Engineering an Empire | Full Episode | History
As we come to the end of our journey through the Ancient Egyptian Dynasties Timeline, we can appreciate the remarkable civilization that flourished for millennia along the Nile River. This timeline has revealed the rise and fall of powerful rulers, the development of monumental architecture, and the advancements in art and technology that characterized this ancient civilization.
By navigating through the dynasties, we have witnessed the pivotal reigns of pharaohs such as Menes, Hatshepsut, and Ramesses II, who left an indelible mark on Egyptian history. The creation of the pyramids and the construction of grand temples stand as a testament to the precision, ingenuity, and deep religious beliefs of the Egyptians.