The Timeline of Indian Dynasties: Navigating the Ebb and Flow of Power takes us on a captivating journey through the rich and complex history of India’s ruling dynasties. From the mighty Mauryas to the powerful Mughals, this timeline unravels the dynamic rise and fall of various empires that shaped India’s cultural, political, and social landscape. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of Indian dynasties and explore the ebbs and flows of power that defined this ancient land.
Spanning over thousands of years, the history of Indian dynasties is a tapestry woven with conquests, alliances, and transitions of power. From the grandeur of the Gupta Empire, known as the “Golden Age” of India, to the fragmentation of the Delhi Sultanate during the medieval period, the timeline reveals the intricate interplay between empires, kingdoms, and dynasties. One significant aspect of this timeline is the ever-changing landscape of religious influence, with empires embracing and patronizing different faiths, such as Buddhism, Hinduism, and Islam. This historical account sheds light on the diverse and dynamic nature of India’s past, offering valuable insights into the ebb and flow of power that continues to shape the present and future of this great nation.
The timeline of Indian dynasties offers a captivating journey through centuries of power shifts and cultural milestones. From the Maurya Empire to the Mughal Empire and the British Raj, each dynasty left its mark on India’s history. Explore the rise and fall of these rulers, their contributions to art, architecture, and governance. Discover how the ebb and flow of power shaped India into the diverse nation it is today.
Contents
- Understanding the Timeline of Indian Dynasties
- Timeline of Indian Dynasties
- Key Takeaways:
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What were the major dynasties that ruled India?
- 2. How did power shift between the dynasties?
- 3. How did cultural and societal dynamics influence power shifts?
- 4. What were the consequences of power shifts between dynasties?
- 5. How does understanding the timeline of Indian dynasties contribute to our knowledge of Indian history?
- THE HISTORY OF INDIA in 12 Minutes – Part 1
Understanding the Timeline of Indian Dynasties
The history of India is marked by the rise and fall of numerous dynasties that shaped the country’s political landscape over thousands of years. The timeline of Indian dynasties is a captivating journey through the ebb and flow of power, encompassing various empires and kingdoms. Each dynasty brought its own unique contributions, leaving an indelible mark on India’s culture, art, and architecture. To navigate this vast timeline is to unlock the secrets of India’s rich and diverse heritage.
Indus Valley Civilization (3300–1300 BCE)
The earliest known civilization in India, the Indus Valley Civilization, was flourishing as early as 3300 BCE. It was characterized by well-planned cities with sophisticated drainage systems, brick houses, and a system of writing that is yet to be fully deciphered. The major cities of Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro were the center of this civilization, which spanned parts of modern-day Pakistan and northwest India.
The decline of the Indus Valley Civilization remains a mystery, with theories ranging from natural disasters to migration and changes in the river systems. Despite its decline, the Indus Valley Civilization left behind a legacy of advanced urban planning and a flourishing agricultural economy.
It is important to note that the Indus Valley Civilization was not a dynasty but a complex cultural entity that predates the concept of dynasties.
Key Points:
- Flourished from 3300 to 1300 BCE.
- Cities with advanced urban planning and drainage systems.
- Major cities like Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro.
- Decline is still a mystery.
Notable Kings/Queens:
- None as it predated the concept of dynasties.
Maurya Dynasty (321–185 BCE)
One of the most influential dynasties in Indian history, the Maurya Dynasty, emerged in 321 BCE under the leadership of Chandragupta Maurya. It reached its zenith under the rule of Emperor Ashoka, who is known for his conversion to Buddhism and promotion of non-violence.
The Maurya Dynasty expanded its empire to include vast territories, from present-day Afghanistan in the west to Bangladesh in the east. It was known for its efficient administrative system, with a centralized authority and a vast network of spies.
The decline of the Maurya Dynasty began after Ashoka’s death, with subsequent weak rulers and external invasions contributing to its ultimate downfall. Nonetheless, the Maurya Dynasty’s impact on Indian history cannot be overstated, particularly through Ashoka’s role in spreading Buddhism.
Key Points:
- Ruled from 321 to 185 BCE.
- Expanded empire across South Asia.
- Known for an efficient administrative system.
- Decline caused by weak rulers and invasions.
Notable Kings/Queens:
- Chandragupta Maurya
- Ashoka
Gupta Dynasty (320–550 CE)
The Gupta Dynasty is considered the Golden Age of India, renowned for its significant advances in science, mathematics, art, and literature. This period witnessed remarkable achievements in fields such as medicine, astronomy, and metallurgy, solidifying India’s position as a center of knowledge.
Under the Gupta Dynasty, India experienced a period of political stability and economic prosperity. The Gupta emperors, known for their patronage of the arts and learning, attracted scholars and artists from all over the world. It was during this time that the famous Iron Pillar of Delhi, known for its rust-free composition, was erected.
The decline of the Gupta Dynasty can be attributed to various factors, including invasions from the Huns and internal conflicts. By the 6th century CE, the Gupta Empire disintegrated into smaller regional kingdoms.
Key Points:
- Ruled from 320 to 550 CE.
- Golden Age of Indian civilization.
- Significant advancements in science, mathematics, and arts.
- Decline caused by invasions and internal conflicts.
Notable Kings/Queens:
- Chandragupta I
- Samudragupta
- Chandragupta II
Delhi Sultanate (1206–1526 CE)
The Delhi Sultanate marked a significant shift in Indian history with the establishment of Islamic rule in northern India. It was founded by Qutb-ud-din Aibak, a general of Muhammad Ghori, in 1206 CE. The Delhi Sultanate witnessed a series of rulers from various dynasties, including the Mamluks, Khaljis, Tughlaqs, and Sayyids.
During the Delhi Sultanate period, Islam spread further in the Indian subcontinent, and Persian culture exerted its influence on art, literature, and architecture. The impressive Qutub Minar in Delhi stands as a testament to the architectural marvels of the Delhi Sultanate.
The decline of the Delhi Sultanate can be attributed to several factors, including regional rebellions, invasions by Mongols and Timur, and the rise of regional kingdoms. The dynasty was eventually defeated by Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire, in the Battle of Panipat in 1526 CE.
Key Points:
- Ruled from 1206 to 1526 CE.
- Islamic rule in northern India.
- Spread of Islam and Persian cultural influence.
- Decline caused by rebellions, invasions, and rise of regional kingdoms.
Notable Kings/Queens:
- Qutb-ud-din Aibak
- Iltutmish
- Alauddin Khalji
- Mohammed bin Tughlaq
India’s history is a tapestry woven with the threads of numerous dynasties. From the Indus Valley Civilization to the Delhi Sultanate, each era had its own unique contributions and influences. Exploring the timeline of Indian dynasties allows us to delve into the diverse and fascinating heritage of a nation that has withstood the test of time. It is through understanding these historical contexts that we can truly appreciate the richness and complexity of India’s cultural mosaic.
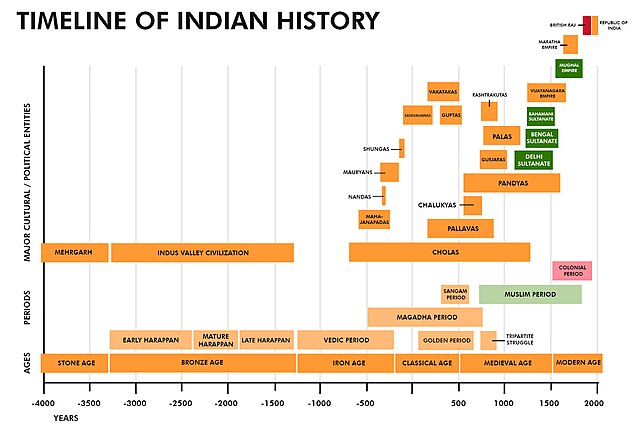
Timeline of Indian Dynasties
The history of India is marked by the rise and fall of various dynasties that ruled the subcontinent. This timeline provides a chronological overview of the major Indian dynasties, highlighting their significant contributions and the ebb and flow of power they experienced.- Maurya Dynasty (322 BCE – 185 BCE): Established by Chandragupta Maurya, this dynasty saw the unification of most of India for the first time under the rule of Emperor Ashoka.
- Gupta Empire (320 CE – 550 CE): Known as India’s golden age, the Gupta Empire witnessed advancements in art, science, and mathematics, along with the spread of Hindu culture.
- Delhi Sultanate (1206 CE – 1526 CE): The Turkish and Afghan dynasties ruled over Delhi, introducing Islamic influence and shaping the course of Indian history.
- The Mughal Empire (1526 CE – 1857 CE): Led by powerful rulers like Akbar, Jahangir, and Shah Jahan, the Mughals established a rich and diverse empire that left a lasting architectural and cultural legacy.
- The British Raj (1858 CE – 1947 CE): With the Indian Rebellion of 1857, the British East India Company was replaced by direct British rule, greatly impacting India’s political and social landscape.
Key Takeaways:
- The Indian subcontinent has been home to numerous dynasties that have risen and fallen throughout history.
- The Maurya Dynasty, founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, was one of the first mighty empires to rule over a large part of India.
- The Gupta Dynasty, known as the “Golden Age” of India, flourished from the 4th to the 6th century CE.
- The Mughal Dynasty, led by powerful emperors such as Akbar, Shah Jahan, and Aurangzeb, ruled over a vast empire in India from the 16th to the 19th century CE.
- The British Raj, a colonial era, had a significant impact on Indian history. It lasted from 1858 to 1947.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about the timeline of Indian dynasties and the ebb and flow of power:
1. What were the major dynasties that ruled India?
The major dynasties that ruled India throughout history include the Maurya, Gupta, Chola, Mughal, and Maratha dynasties. Each of these dynasties had a significant impact on Indian history, leaving their mark on politics, culture, and society.
During their reigns, these dynasties experienced periods of prosperity and expansion, as well as periods of decline and fragmentation. Understanding the timeline of these dynasties can provide valuable insights into the ebb and flow of power in Indian history.
2. How did power shift between the dynasties?
Power in India’s history often shifted between dynasties through conquest, alliances, and the rise and fall of individual rulers. Strong dynasties would expand their territories through military campaigns, while weaker ones would be conquered or absorbed into more powerful kingdoms.
Additionally, political marriages, the establishment of alliances, and the patronage of powerful regional leaders also played a role in the transfer of power between dynasties. These dynamics contributed to the ever-changing landscape of political authority in India.
3. How did cultural and societal dynamics influence power shifts?
Cultural and societal dynamics played a crucial role in power shifts between Indian dynasties. The spread of religious beliefs, such as Buddhism and Hinduism, would often influence the political landscape. Dynasties that aligned themselves with popular religious movements would gain the support of the masses, solidifying their power.
Furthermore, the economic prosperity and cultural advancements of certain regions or cities under the rule of a particular dynasty would attract talent, intellectuals, and migrants, contributing to the overall strength of the kingdom. These societal factors had a significant impact on the ebb and flow of power in Indian dynasties.
4. What were the consequences of power shifts between dynasties?
The consequences of power shifts between dynasties in Indian history were diverse. When a powerful dynasty rose to prominence, it would often bring stability, economic growth, and cultural flourishing to the region under its rule. This led to advancements in architecture, art, literature, and other areas of human endeavor.
Conversely, when a dynasty declined or was overthrown, it often resulted in political instability, economic decline, and social unrest. These transitions could sometimes be violent, leading to significant upheaval and the restructuring of power dynamics in India.
5. How does understanding the timeline of Indian dynasties contribute to our knowledge of Indian history?
Understanding the timeline of Indian dynasties provides a comprehensive view of the historical development of India. It sheds light on the political, cultural, and social transformations that have shaped the country over centuries.
By examining the rise and fall of dynasties, their achievements and failures, and the factors that influenced power shifts, we gain a deeper understanding of India’s complex history. This knowledge allows us to appreciate the rich heritage and diversity of present-day India and recognize the enduring influence of these dynasties on modern society.
THE HISTORY OF INDIA in 12 Minutes – Part 1
Throughout the rich history of India, numerous dynasties have risen and fallen, each leaving their mark on the landscape of power. From the Mauryas to the Mughals, these dynasties shaped the trajectory of the subcontinent, forever leaving a lasting legacy. This timeline of Indian dynasties offers a glimpse into the ebb and flow of power that has defined the region.
From the grandeur of the Gupta Empire to the reign of the Cholas, each dynasty brought its unique cultural, political, and economic contributions to India. We witnessed the development of magnificent architectural wonders like the Taj Mahal under the Mughals, the spread of Buddhism during the time of the Mauryas, and the emergence of vibrant trade networks during the time of the Vijayanagara Empire.