When comparing the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire, it is intriguing to explore the similarities and differences between these two powerful civilizations. One surprising fact is that despite being geographically and culturally distinct, both the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire had lasting impacts on the world, shaping the course of history in their respective regions. From military strategies to political structures, to advancements in technology and trade, these two great empires left enduring legacies that continue to be studied and admired today.
In terms of history and background, the Han Dynasty and Roman Empire held significant positions of power during their time. The Han Dynasty, which ruled over China for over four centuries, saw remarkable advancements in agriculture, literature, and philosophy. Embracing Confucian principles, the Han Dynasty built a centralized bureaucratic system and developed an extensive network of trade routes, known as the Silk Road. On the other hand, the Roman Empire, which spanned three continents, adopted a system of governance that included a republican framework and later transitioned into an imperial autocracy. With their engineering marvels, such as aqueducts and roads, and their legal system, the Romans left an indelible mark on European civilization. These historical backgrounds, coupled with unique cultural expressions and social structures, make the comparison between the Han Dynasty and Roman Empire a fascinating topic of study.
The Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire were two powerful civilizations that existed during different time periods. While both empires had significant military and political influence, there were some key differences in their governance, culture, and social structure. The Han Dynasty was characterized by its centralized government, Confucian philosophy, and civil service examination system. On the other hand, the Roman Empire was known for its decentralized administration, legal system, and influential contributions to art and architecture. Despite these differences, both empires left a lasting impact on world history.

Contents
- The Sociopolitical Structures of the Han Dynasty and Roman Empire
- Economic Systems: Agrarian vs. Trade
- Han Dynasty vs Roman Empire: A Comparative Analysis
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What were the main differences between the social structures of the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire?
- 2. What were the key differences in government and administration between the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire?
- 3. How did trade and economy differ between the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire?
- 4. What were the main architectural and artistic styles of the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire?
- 5. What were the major factors that led to the decline and fall of the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire?
The Sociopolitical Structures of the Han Dynasty and Roman Empire
The Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire were two powerful civilizations that existed during the same time period in different parts of the world. While they were separated by vast distances and cultural differences, both empires experienced significant political and social developments. This article will analyze the sociopolitical structures of the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire, comparing and contrasting their systems of governance, administration, and social hierarchies.
Governance
The Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire had distinct systems of governance. The Han Dynasty was an autocratic monarchy ruled by a single emperor who had absolute power. The emperor was considered the Son of Heaven and the ultimate authority in the empire. The emperor appointed officials to govern different regions and relied on a complex bureaucracy to manage state affairs. The bureaucracy consisted of civil servants who were selected through a rigorous examination system based on Confucian principles.
On the other hand, the Roman Empire had a mixed system of government that evolved over time. Initially, Rome was a republic with a Senate that represented the interests of the patrician class. However, as the empire expanded, power shifted towards the emperors, who held both military and political authority. The emperors appointed governors to administer the various provinces, but they also relied on the Senate for advice and support.
It is important to note that while both empires had centralized systems of governance, the way power was distributed and exercised differed significantly. The Han Dynasty relied heavily on a centralized bureaucracy, whereas the Roman Empire had a more decentralized system with power shared between the emperors and the Senate.
Administration
In terms of administration, the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire had different approaches. The Han Dynasty adopted a highly organized administrative system with a hierarchical structure. The empire was divided into provinces, and each province was governed by a governor appointed by the emperor. The governors were responsible for maintaining law and order, collecting taxes, and overseeing local affairs. They reported directly to the central government.
The Roman Empire, on the other hand, had a more flexible administrative system. The emperors appointed governors to oversee the provinces, but these governors often had more autonomy and were given greater decision-making powers compared to their counterparts in the Han Dynasty. The Roman Empire also delegated certain responsibilities to local elites, allowing them to participate in the governance of their respective regions.
Despite these differences, both empires relied on a system of taxation to sustain their administrative infrastructure. Taxes were collected from the population and used to fund various public projects, such as infrastructure development, military expenditures, and social welfare programs.
Social Hierarchies
Another important aspect to consider when comparing the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire is their social hierarchies. In both empires, social status was largely determined by birth, but there were some key differences in the way social classes were structured.
The Han Dynasty had a rigid social hierarchy that was based on Confucian principles. At the top of the social ladder were the emperor and the imperial family, followed by the aristocracy and officials. Below them were the peasants, who constituted the majority of the population, and at the bottom were merchants and artisans. Social mobility was limited in the Han Dynasty, as one’s social status was mostly determined by birth.
In contrast, the Roman Empire had a more fluid social hierarchy. While birth played a role in determining social status, there was greater opportunity for upward mobility. Roman society was divided into several classes, including the senatorial class, the equestrian class, and the plebeians. Slaves and freedmen occupied the lowest rungs of society, but even they had the potential to improve their circumstances through various means, such as education, military service, or entrepreneurship.
It is worth noting that despite these differences, both the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire granted privileges and advantages to the ruling class and were characterized by significant social inequalities.
Economic Systems: Agrarian vs. Trade
The economic systems of the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire were shaped by their geographical and cultural contexts. While both empires relied on agriculture as a primary economic activity, there were distinct differences in their approach to commerce and trade.
Agrarian Economies
The Han Dynasty was primarily an agrarian society. Agriculture was the backbone of the economy, and the majority of the population relied on farming for their livelihood. The government played a crucial role in agricultural production, implementing policies to ensure food security and regulate land distribution. The Han Dynasty introduced advanced farming techniques, such as the widespread use of iron tools and the cultivation of new crops like rice, which significantly increased agricultural productivity.
The Roman Empire also had an agrarian economy, but it was less reliant on agriculture compared to the Han Dynasty. While farming was important, the Roman Empire had a more diversified economy that encompassed trade, manufacturing, and mining. The empire benefited from its vast territorial holdings, which provided access to various natural resources and trade routes.
Both empires implemented policies to support their agricultural sectors and ensure food supply. They built irrigation systems, constructed roads, and provided incentives for farmers to increase productivity. However, the Han Dynasty focused more on self-sufficiency, while the Roman Empire actively engaged in trade and sought to expand its economic reach beyond its borders.
Trade and Commerce
The Roman Empire had a flourishing trade network that extended across Europe, the Mediterranean, and into Asia. Trade was a vital part of the Roman economy, and the empire relied on imports of luxury goods, raw materials, and foodstuff from its provinces and beyond. Rome itself became a major center of trade and commerce.
The Han Dynasty also engaged in trade, but its focus was primarily on domestic commerce rather than international trade. The Silk Road, a network of ancient trade routes connecting China to the West, played a significant role in facilitating trade between the Han Dynasty and other civilizations. The empire exported silk, tea, and other luxury goods, while importing precious metals, spices, and exotic animals.
The Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire both benefited from their economic activities, but their emphasis on different economic sectors influenced their respective development trajectories.
Impact on Society
The economic systems of the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire had a profound impact on their societies. In the Han Dynasty, the agrarian economy reinforced the importance of the family unit and the values of filial piety and loyalty. Agriculture was not only an economic activity but also a cultural cornerstone.
On the other hand, the Roman Empire’s diverse economic activities and the flourishing trade network contributed to the rise of a cosmopolitan society. The empire’s economic prosperity attracted people from various regions, leading to cultural exchanges and the spread of ideas.
In conclusion, while both the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire had agrarian economies, the Roman Empire had a more diversified economic system that embraced trade and commerce on a larger scale. Their economic systems had profound effects on their respective societies, shaping values, cultural practices, and social structures.
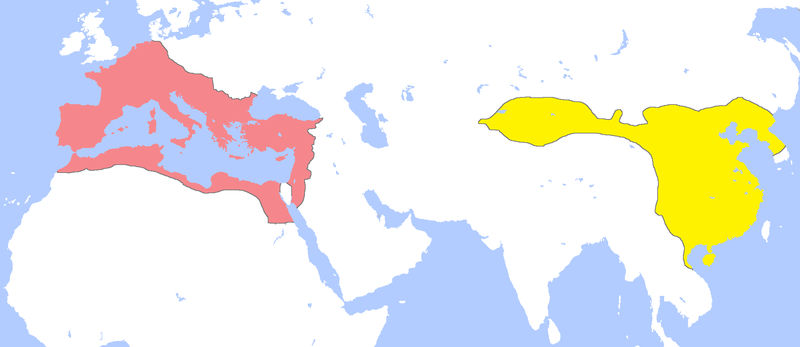
Han Dynasty vs Roman Empire: A Comparative Analysis
- The Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire were two of the most powerful and influential civilizations in ancient history.
- Both empires spanned vast territories and lasted for centuries, leaving a lasting impact on the world.
- The Han Dynasty, which ruled China from 206 BCE to 220 CE, was known for its centralized government, Confucian ideology, and advancements in technology and agriculture.
- The Roman Empire, which lasted from 27 BCE to 476 CE, was characterized by its republican roots, military prowess, and engineering achievements.
- One major difference between the two empires was their form of government. The Han Dynasty had a centralized bureaucracy, while the Roman Empire had a combination of a republic and an autocratic monarchy.
- Another difference was their religious practices. The Han Dynasty followed Confucianism and ancestral worship, while the Roman Empire practiced a polytheistic religion with a pantheon of gods.
- The two empires also differed in their approach to expansion. The Han Dynasty focused on expanding its influence through diplomacy and maintaining tributary relationships, while the Roman Empire relied heavily on military conquest.
- Despite these differences, both the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire had a strong emphasis on trade and commerce, which fueled their economies and facilitated cultural exchange.
- In conclusion, the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire were distinct civilizations, each with its own unique characteristics and contributions to the world. Understanding their similarities and differences allows us to gain valuable insights into the complexities of ancient civilizations.
Key Takeaways
- The Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire were two powerful civilizations that existed during the same time period.
- Despite their differences in geography, government structure, and culture, both civilizations achieved great success in areas such as engineering, art, and warfare.
- The Han Dynasty emphasized agriculture, Confucianism, and centralized government control, while the Roman Empire focused on trade, military conquest, and a republican system of government.
- The collapse of the Han Dynasty and the decline of the Roman Empire were caused by internal conflicts, invasions from outside forces, and economic instability.
- Comparing the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire provides valuable insights into the diversity and complexity of human civilizations and the factors that contribute to their rise and fall.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire were two of the most powerful and influential civilizations in history. Both empires had a significant impact on their respective regions and left behind a rich cultural and historical legacy. In this comparative analysis, we will explore some frequently asked questions about the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire to better understand their similarities and differences.The social structure of the Han Dynasty in China was primarily based on the principles of Confucianism. It consisted of four main classes: scholars, farmers, artisans, and merchants. The scholars or Confucian elites held the highest social status and were responsible for governing the empire. Farmers were considered the backbone of society and played a crucial role in agricultural production. Artisans and merchants had a lower social status but were still respected members of society.
In contrast, the social structure of the Roman Empire was divided into two main classes: the patricians and the plebeians. The patricians were the wealthy aristocracy who held most of the power and political offices. The plebeians, on the other hand, were the common people, including farmers, artisans, and laborers. Despite this divide, social mobility was possible in the Roman Empire, with plebeians having the opportunity to gain wealth and status through military service or successful business ventures.
2. What were the key differences in government and administration between the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire?
The Han Dynasty had a centralized bureaucratic government, with the emperor as the ultimate authority. The emperor appointed officials based on their merit and competence, and they were responsible for governing various regions and implementing policies. The administration of the Han Dynasty relied heavily on the Confucian principles of benevolent rule and harmony.
The Roman Empire, on the other hand, had a system of government known as a republic, where power was initially shared between the Senate, the aristocracy, and the people. Eventually, the Roman Empire transitioned to a centralized autocracy, with the emperor having absolute power. The administration of the Roman Empire focused on maintaining order, expanding territories, and maintaining the loyalty of the military.
3. How did trade and economy differ between the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire?
Trade played a vital role in both the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire. The Han Dynasty had a thriving trade network known as the Silk Road, which connected China with Central Asia and the Mediterranean. This facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural influences.
The Roman Empire, on the other hand, had an extensive trade network that spanned Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. The Romans were known for their advanced transportation infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and ports. The economy of the Roman Empire relied heavily on trade and agriculture.
4. What were the main architectural and artistic styles of the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire?
The Han Dynasty is known for its impressive architectural structures, such as the Great Wall of China and the magnificent tombs of the emperors. The Han Dynasty also excelled in the art of bronze casting, jade carving, and pottery.
The Roman Empire is renowned for its architectural marvels, including iconic structures like the Colosseum, aqueducts, and amphitheaters. Roman art encompassed various styles, including realistic sculptures, colorful frescoes, and intricate mosaics.
5. What were the major factors that led to the decline and fall of the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire?
Several factors contributed to the decline and fall of the Han Dynasty, including political corruption, regional rebellions, economic instability, and the invasion of nomadic tribes from the north. These challenges weakened the central government and eventually led to the collapse of the dynasty.
The fall of the Roman Empire was a complex process influenced by various factors. These include political instability, economic decline, invasions by barbarian tribes, internal conflicts, and the division of the empire into the Western and Eastern Roman Empires. The Western Roman Empire eventually succumbed to these pressures and was overrun by barbarian invasions, leading to its downfall.
Overall, the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire were two prominent civilizations that existed around the same time period but had distinct characteristics and achievements. The Han Dynasty, located in China, was known for its centralized government, strong bureaucracy, and advancements in arts, science, and technology. On the other hand, the Roman Empire, situated in Europe, boasted a vast empire with a strong military, impressive infrastructure, and significant influence on law, language, and culture.
While both civilizations had their unique strengths and contributions, they also faced their fair share of challenges. The Han Dynasty struggled with corruption within the government and occasional rebellions, whereas the Roman Empire faced decline due to economic problems, invasions, and political instability. Despite these differences and challenges, the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire both left a lasting impact on history, shaping the development of their respective regions and influencing subsequent civilizations.