Persia, known as one of the greatest empires in ancient history, had a remarkable system of governance that allowed it to effectively rule over its vast territories. With an empire extending from present-day Iran to Egypt and Greece, Persia faced the challenge of governing diverse societies and cultures. How did Persia manage to maintain control and stability over such a large empire? Let’s explore the fascinating methods and strategies employed by the Persian rulers.
The governance of Persia was characterized by a centralized system that emphasized efficient administration and political organization. At the heart of their governance was the concept of satraps, which were provincial governors responsible for overseeing specific regions of the empire. This system allowed for local autonomy to a certain extent, while still maintaining overall control and ensuring loyalty to the central authority. By appointing trusted individuals as satraps, Persia was able to maintain stability and enforce their laws and policies throughout the empire. Additionally, the Persians practiced religious tolerance and allowed conquered peoples to retain their own customs and traditions, fostering a sense of unity and minimizing resistance against their rule. Through these methods, Persia was able to effectively govern its large empire and maintain its dominance for centuries.
Persia governed its large empire through a centralized administration system that allowed for efficient governance. The empire was divided into provinces, each governed by a satrap who reported to the king. The satraps were responsible for collecting taxes, maintaining order, and ensuring the loyalty of their regions. The king appointed trusted officials to oversee the empire’s different sectors, including finance, military, and justice. Decentralized power structures and the use of local customs helped maintain stability and control.
Contents
- Persian Satraps: An Efficient System of Administration
- Persia’s Governance of Its Vast Empire
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did the Persian Empire manage its large empire?
- 2. How did the Persian Empire maintain control over its diverse population?
- 3. What role did the king play in governing the Persian Empire?
- 4. How did the Persian Empire ensure efficient communication and trade across its vast territories?
- 5. Did the Persian Empire use any administrative or bureaucratic systems?
Persian Satraps: An Efficient System of Administration
A unique aspect of how Persia governed its large empire was through the use of satraps, who played a crucial role in the administration and governance of the vast Persian territories. Satraps were provincial governors appointed by the Persian emperor, known as the Great King. This system of administration allowed Persia to maintain control over its diverse and expansive empire, ensuring effective governance, resource management, and the collection of tribute.
Appointment and Responsibilities of Satraps
The satraps were appointed by the Persian emperor based on their loyalty, trustworthiness, and administrative abilities. They were expected to be the extension of the emperor’s power and authority in their respective provinces. Their responsibilities included maintaining law and order, collecting taxes and tribute, supervising local officials, and managing the allocation of resources. The satraps acted as intermediaries between the Persian royal court and the local populations, ensuring the smooth functioning of the empire.
Each satrap governed a specific province and had significant autonomy in managing the affairs of their region. However, they were also accountable to the Persian emperor and his central administration. The satraps were required to send regular reports to the royal court, updating the emperor on the state of the province, any major events or issues, and the collection of tribute. This system of reporting helped ensure transparency and enabled the central administration to monitor the overall functioning of the empire.
To maintain loyalty and prevent rebellions, the Persian emperor employed a system of checks and balances on the satraps. Spies and secret agents were often used to monitor the activities of the satraps and ensure their adherence to imperial policies. This system helped curb corruption and dissent within the local administration, ensuring the stability and continuity of Persian rule in the empire.
The Royal Road: Efficient Communication and Trade Network
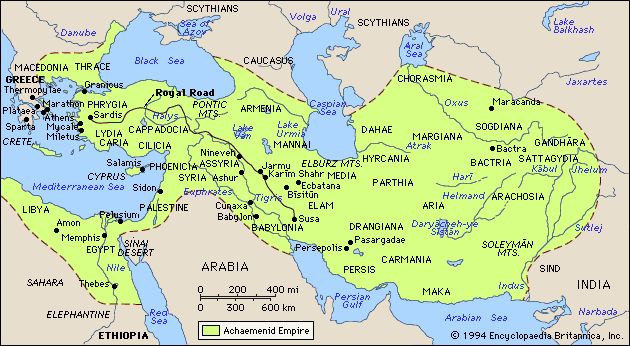
Another remarkable aspect of Persian governance was the establishment of the Royal Road, an extensive network of roads and courier stations that spanned across the empire. Built during the reign of Darius the Great, the Royal Road facilitated efficient communication, trade, and the rapid movement of troops and officials throughout the empire.
The Royal Road served as a vital link between the central administration in Persia and the far-flung provinces. It enabled the swift delivery of royal decrees, imperial orders, and messages between the emperor and the satraps. This facilitated centralized decision-making, effective governance, and coordination between the various regions of the empire.
In addition to its administrative function, the Royal Road played a crucial role in promoting trade and commerce within the Persian Empire. The road connected major trade cities and markets, ensuring the smooth flow of goods, ideas, and cultural exchange. This contributed to economic prosperity and cultural diversity within the empire, further solidifying Persian control over its vast territories.
The Royal Road was a remarkable feat of engineering for its time, stretching over 2,500 kilometers from Sardis in modern-day Turkey to Susa in present-day Iran. It was equipped with well-maintained rest stations, postal stations, and relays of couriers, allowing for rapid communication and efficient travel. The upkeep and protection of the Royal Road were of utmost importance to the Persian administration, demonstrating their commitment to maintaining effective governance and communication within the empire.
The Use of Local Laws and Customs
Persia recognized the importance of respecting local laws, customs, and cultures within its large empire. Rather than imposing a homogenous legal system, Persian governance allowed for a degree of autonomy in local laws and traditions. This flexible approach to governance helped foster stability and harmony within the diverse regions of the empire.
The satraps, in consultation with local advisors and officials, often incorporated local customs and traditions into their administrative practices. This ensured that the governance of each province respected the unique cultural, religious, and social norms of the local population. By embracing diversity and accommodating local practices, Persian rule was able to gain the acceptance and loyalty of its subjects, further strengthening its control over the empire.
At the same time, Persia maintained a centralized legal framework that operated alongside local laws. The Persian emperor, supported by a council of advisors, issued decrees and rulings that guided the overall legal system of the empire. This helped maintain consistency and fairness in the application of laws while allowing for the necessary flexibility needed to accommodate local customs.
The Role of Medes and Cyrus the Great in Persian Governance
The rise of the Persian Empire can be attributed to the leadership of Cyrus the Great and the influence of the Medes. The Medes, an ancient Iranian people, played a crucial role in laying the foundation for Persian governance. Cyrus the Great, the founder of the Persian Empire, was initially the king of Anshan, a vassal state under Median control.
After the fall of the Median Empire, Cyrus seized the opportunity to unite the various Persian tribes and rebel against Median rule. His successful campaign, supported by the Medes, led to the establishment of the Persian Empire. Cyrus embraced the diverse cultures and religions of his subjects, allowing for the coexistence of different ethnic groups within the empire.
Cyrus the Great implemented a policy of religious and cultural tolerance, which played a significant role in maintaining stability and harmony within the empire. He issued the famous Cyrus Cylinder, considered one of the earliest documents advocating for human rights, granting freedom to conquered peoples and allowing them to practice their own religions and retain their cultural identities.
The Legacy of Persian Governance
The Persian Empire left a lasting legacy in terms of governance and administration. Its innovative administrative system, utilizing satraps, facilitated effective governance and resource management in a large and diverse empire. The establishment of the Royal Road enabled efficient communication and trade, further strengthening the cohesion of the empire. Additionally, the accommodation of local laws and customs and the promotion of religious and cultural tolerance helped foster stability and acceptance within the empire.
The governance techniques employed by Persia continue to influence modern systems of administration. The Persian Empire serves as a historical example of successful governance and efficient management of a vast and diverse empire. By understanding how Persia governed its large empire, we can gain valuable insights into the complexities of governing vast territories and maintaining stability in diverse societies.
Persia’s Governance of Its Vast Empire
Persia, known for its grand empire, implemented a sophisticated system of governance to effectively rule its vast lands. At the center of this system was the Persian king, who held absolute power and was revered as a god-like figure. Surrounding the king were a group of noble advisors, known as the satraps, who governed specific regions on the king’s behalf.
One of the key pillars of Persian governance was a well-organized administrative structure. This structure consisted of various departments responsible for different aspects of governance, such as collecting taxes, maintaining law and order, and overseeing infrastructure development. The system also included an efficient communication network, with a complex system of messengers and relays to ensure swift transmission of information throughout the empire.
The Persians also implemented a policy of cultural and religious tolerance. While they allowed local customs and traditions to persist, they emphasized the importance of loyalty to the empire. They built a network of roads and infrastructure to facilitate trade and communication, promoting economic growth and stability.
In summary, Persia governed its vast empire through a centralized system of power, supported by a well-structured administrative framework, effective communication networks, cultural tolerance, and economic development. This combination of strong leadership and efficient governance contributed to the empire’s stability and prosperity for centuries.
Key Takeaways
- Persia governed its large empire through a decentralized administrative system.
- The empire was divided into provinces, each governed by a satrap appointed by the king.
- Satraps had to collect taxes, maintain order, and ensure loyalty to the king.
- Communication and trade were facilitated by a well-developed road network.
- The royal guard, known as the Immortals, helped maintain security and enforce the king’s authority.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we will explore some frequently asked questions about how the Persian Empire governed its vast territories.
1. How did the Persian Empire manage its large empire?
The Persian Empire employed a variety of strategies to manage its large empire. One of the key methods was the establishment of a centralized administration. The empire was divided into provinces, each governed by a satrap who acted as a regional governor. The satraps were hand-picked by the king and were responsible for collecting taxes, maintaining order, and ensuring loyalty to the empire. Additionally, the Persian Empire practiced religious tolerance, allowing conquered peoples to continue practicing their own religions, which helped to maintain stability.
Another important aspect of Persian governance was the use of a standardized legal code. Known as the “Law of the Medes and Persians,” this code ensured uniformity in legal matters throughout the empire. The code was based on principles of fairness and justice and aimed to protect the rights of both the ruler and the ruled. The Persian Empire also employed an efficient communication system, including the use of royal road networks, to facilitate the flow of information and goods across its vast territories.
2. How did the Persian Empire maintain control over its diverse population?
The Persian Empire maintained control over its diverse population through a combination of cultural and political strategies. The empire practiced a policy of religious tolerance, allowing conquered peoples to continue practicing their own religions. This policy helped to create a sense of inclusion and reduce resistance from different religious groups. The Persian Empire also encouraged cultural exchange and assimilation, adopting elements from the cultures of conquered peoples and incorporating them into its own administrative and artistic practices.
Politically, the Persian Empire employed a system of decentralized governance. While the empire was centrally administered, regional governors known as satraps were given autonomy in their territories, as long as they remained loyal to the empire. This allowed the empire to effectively govern its diverse population by delegating power and allowing local customs and traditions to be preserved. Additionally, the empire employed a system of tribute, where conquered territories paid taxes and provided resources to the empire in exchange for protection and economic benefits.
3. What role did the king play in governing the Persian Empire?
The king played a central role in governing the Persian Empire. As the absolute ruler, the king had ultimate authority and power. The king was responsible for appointing the satraps, who acted as his representatives in the provinces. The king also played a role in the administration of justice, ensuring that the laws of the empire were upheld and fairness was maintained. Additionally, the king was the commander-in-chief of the military and played a crucial role in defending the empire from external threats.
Furthermore, the king played a significant religious role in the empire. The Persian kings were considered divine or semi-divine figures, and their rule was seen as ordained by the gods. This religious authority gave the kings legitimacy and helped to maintain loyalty and obedience among the people. The king also played a role in promoting and patronizing religious practices, temples, and rituals, which further solidified their rule.
4. How did the Persian Empire ensure efficient communication and trade across its vast territories?
The Persian Empire employed several measures to ensure efficient communication and trade across its vast territories. One of the most notable initiatives was the construction of a network of royal roads. These roads connected the major cities and administrative centers of the empire, allowing for the swift movement of messengers, officials, and goods. The use of standardized currency, known as the daric, also facilitated trade by providing a common medium of exchange.
Additionally, the Persian Empire maintained a system of waystations along the royal roads, where travelers could rest, refresh, and exchange horses. These waystations ensured a steady flow of communication and helped to maintain law and order along the roads. The empire also employed a system of courier services, where messengers on horseback would travel between the major cities to deliver important messages and decrees.
5. Did the Persian Empire use any administrative or bureaucratic systems?
Yes, the Persian Empire had a complex administrative and bureaucratic system in place to govern its large empire. The empire was divided into provinces known as satrapies, each governed by a satrap who served as a regional governor. The satraps were responsible for collecting taxes, maintaining order, and ensuring loyalty to the empire. Below the satraps were local administrators and officials who oversaw specific aspects of governance, such as taxation, public works, and agriculture
Throughout history, the Persian Empire was known for its effective governance of its vast territories. One key aspect of their governance was the use of satraps, who acted as regional governors overseeing different provinces. This decentralized system allowed for local autonomy while ensuring allegiance to the central Persian government.
The Persian Empire also maintained a well-structured administrative system. This included the use of an imperial bureaucracy, with officials responsible for collecting taxes, maintaining public order, and managing infrastructure projects. The empire’s efficient communication system, which involved the use of the Royal Road, facilitated the delivery of messages and goods across the vast empire.