The Khilji Dynasty in India, under the reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji, holds a significant place in history due to its profound impact on the Indian subcontinent. A fascinating aspect of this dynasty is that it marked the first time a non-Indian Muslim dynasty came to power in northern India. This pivotal moment in history reshaped the political and cultural landscape of the region.
The reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji is particularly noteworthy for his effective administration and military achievements. He implemented several progressive policies, such as reforms in revenue administration and market regulation, which led to economic stability and growth. Additionally, his military campaigns expanded the Khilji Dynasty’s territory, establishing dominance over various regions in India. The reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji exemplifies a period of significant transformation and consolidation of power in the Indian subcontinent.
The Khilji Dynasty in India, led by Ala-ud-din Khilji, witnessed significant changes and achievements during his reign. Ala-ud-din Khilji was known for his military conquests and administrative reforms. He introduced various economic policies, including price control measures and market regulations. His reign also saw the construction of iconic structures like the Alai Darwaza and the Qutub Minar. Furthermore, Ala-ud-din Khilji’s military successes expanded the boundaries of the empire. His reign left a lasting impact on the political, economic, and cultural landscape of medieval India.
Contents
- The Rise of Ala-ud-din Khilji
- Impact on Trade and Economy
- Legacy and Influence
- Khilji Dynasty in India: Exploring the Reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Who was Ala-ud-din Khilji and what were his major achievements?
- 2. What were Ala-ud-din Khilji’s major military campaigns?
- 3. How did Ala-ud-din Khilji strengthen the economy during his reign?
- 4. What were Ala-ud-din Khilji’s administrative reforms?
- 5. What was Ala-ud-din Khilji’s impact on Indian society and culture?
- The Khalji Dynasty || Delhi Sultanate || Medieval History || Lec. 8 || An Aspirant !
The Rise of Ala-ud-din Khilji
The Khilji Dynasty in India, especially during the reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji, marked a significant period in Indian history. Ala-ud-din Khilji ascended to the throne in 1296 CE and ruled until 1316 CE. His reign was characterized by military conquests, administrative reforms, and a strong focus on maintaining a centralized authority. Let us explore the various aspects of the Khilji Dynasty and the impactful reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji.
Military Conquests and Expansion
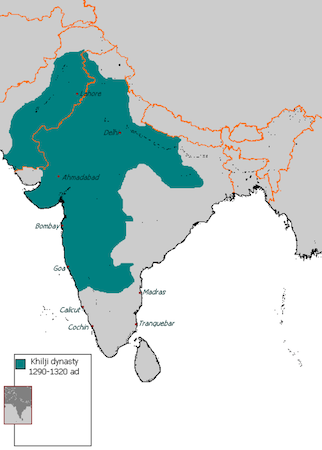
One of the defining features of Ala-ud-din Khilji’s reign was the extensive military campaigns and territorial expansion. He aimed to establish a vast empire and conquer new territories. His armies embarked on successful campaigns against the Yadava Kingdom of Devagiri, Gujarat, and many parts of Southern India. The conquest of the Hindu kingdom of Ranthambore was particularly significant, as it provided access to the rich resources of Central India.
In 1299 CE, Ala-ud-din Khilji set his sights on the powerful Rajput kingdom of Chittor. Despite facing fierce resistance from the Rajputs led by Rana Ratan Singh, Khilji’s forces eventually emerged victorious. The fall of Chittor was followed by the conquest of other Rajput kingdoms, solidifying Khilji’s dominance over Northern India. These military successes not only expanded the Khilji Empire but also brought immense wealth and resources to the treasury.
Ala-ud-din Khilji’s military conquests were characterized by strategic planning, effective use of artillery, and the assimilation of conquered territories into the empire. His military prowess and ambition contributed significantly to the expansion and consolidation of the Khilji Dynasty in India.
Administrative Reforms and Centralization
Parallel to his military conquests, Ala-ud-din Khilji implemented a series of administrative reforms to maintain control and centralize authority within his empire. He established a robust administrative system that focused on efficient revenue administration, efficient governance, and the enhancement of state institutions.
One of the significant reforms introduced by Khilji was the issuance of market regulations, known as the ‘Market Control System’ or ‘Diwani-i-Riyasat.’ These regulations aimed to stabilize prices, prevent hoarding, and ensure the availability of essential commodities to the common people. By controlling prices and trade, Khilji aimed to prevent inflation and maintain social stability.
To strengthen his control over the empire, Ala-ud-din Khilji appointed trusted officials called ‘Amirs’ to key administrative positions. These officials were responsible for revenue collection, law and order, and the overall governance of the provinces. Khilji’s system of delegation and supervision ensured effective administration across the vast empire, enabling him to exercise centralized authority.
Impact on Society and Culture
The reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji left a profound impact on the social and cultural fabric of India. The extensive military campaigns and the assimilation of diverse territories resulted in the integration and interaction of different cultures and traditions. These interactions influenced art, architecture, language, and social practices.
During his reign, Khilji patronized scholars, poets, and artists, leading to a flourishing of literature and art. One of the most significant literary works of the time was the ‘Padmavat,’ a fictionalized epic poem that narrated the tale of Rani Padmini of Chittor and her brave resistance against Ala-ud-din Khilji’s forces. This work highlighted the valor and sacrifice of Rajput warriors, emphasizing the resilience and pride of the Rajput community.
Additionally, the influence of Persian and Islamic traditions grew during the Khilji Dynasty. Persian language and literature gained prominence, and architectural styles infused with Persian elements emerged during this period. The ‘Alai Darwaza’ in the Qutub Complex of Delhi, built by Ala-ud-din Khilji, stands as a striking example of the fusion of Indian and Persian architectural styles.
Legacy and End of the Khilji Dynasty
The reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji marked a significant chapter in the history of the Khilji Dynasty, but it eventually came to an end with his demise in 1316 CE. His successors lacked the strategic brilliance and administrative skills, leading to internal conflicts and external invasions. The central authority weakened, and the empire gradually disintegrated.
Despite its eventual decline, the Khilji Dynasty left a lasting impact on the political, administrative, and cultural spheres of India. The military successes, administrative reforms, and cultural exchanges during the reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji shaped the course of Indian history, paving the way for future dynasties and influencing the socio-cultural landscape of the subcontinent.
Impact on Trade and Economy
The Khilji Dynasty, under the reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji, had a profound impact on the trade and economy of India. His conquests and expansive rule contributed to the growth of a centralized economic system and the establishment of a flourishing trade network.
Control over Trade Routes
Ala-ud-din Khilji’s conquests expanded the geographical boundaries of the Khilji Empire, enabling the control of strategic trade routes. The empire gained access to crucial sea routes, such as the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, facilitating maritime trade with regions like the Middle East and Southeast Asia.
This control over trade routes allowed the Khilji Dynasty to establish commercial relationships with neighboring regions, enhancing economic prosperity and cultural exchanges. The empire became a hub for international trade, attracting merchants and traders from distant lands.
Additionally, the Khilji Dynasty implemented measures to encourage domestic trade. Ala-ud-din Khilji’s market regulations aimed to stabilize prices and maintain a steady supply of goods, ensuring a favorable business environment within the empire. These policies boosted domestic trade and further contributed to economic growth.
Development of Infrastructure
In addition to controlling trade routes, Ala-ud-din Khilji invested in the development of infrastructure to support economic activities. He constructed new roads, bridges, and caravanserais (rest houses for traders) along important trade routes. This infrastructure development facilitated the movement of goods and traders, contributing to the growth of trade and commerce.
The establishment of fortified cities, such as Siri in Delhi, further enhanced the economic potential of the empire. These cities served as centers of trade, administration, and cultural exchange, attracting merchants, artisans, and entrepreneurs. The urban centers thrived with economic activity, leading to increased wealth and prosperity.
Wealth and Taxation
Ala-ud-din Khilji’s military conquests and meticulous administration brought immense wealth to the empire. The surplus revenue generated through taxation of conquered territories, including land revenue and the imposition of various taxes, bolstered the treasury.
Khilji implemented a strict taxation system to maximize revenue. He introduced measures such as the ‘Zakat’ and ‘Jizya,’ which were taxes imposed on Muslims and non-Muslims, respectively. The revenue generated from these taxes, along with other forms of taxation, funded the empire’s military campaigns, infrastructure development, and patronage of arts and culture.
The accumulation of wealth and the conducive economic climate during the Khilji Dynasty contributed to a flourishing economy, attracting traders, craftsmen, and merchants from various regions. The empire experienced a period of prosperity and economic growth, leaving a lasting impact on the trade and economy of India.
Legacy and Influence
The reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji and the Khilji Dynasty left a lasting legacy and exerted significant influence on various aspects of Indian history.
Military Tactics and Strategies
Ala-ud-din Khilji’s military campaigns showcased his strategic brilliance and introduced innovative tactics. His use of siege warfare, the employment of superior artillery, and the creation of a disciplined military force set a precedent for future military leaders in India. The military strategies employed by Khilji influenced subsequent rulers, shaping the course of warfare in the subcontinent.
The military reforms introduced by Khilji, such as the use of the ‘Hazar Sena’ or ‘Thousand Strong Army,’ a specialized force of 1,000 soldiers, demonstrated the importance of a professional army in achieving military dominance. These military innovations laid the foundation for future military structures and strategies in India.
Cultural Exchanges and Architecture
The cultural exchanges during the Khilji Dynasty resulted in the fusion of Indian and Persian artistic and architectural styles. The architectural marvels of this period, such as the Qutub Complex and the Alai Darwaza, exhibit the influence of Persian aesthetics on the indigenous Indian architectural traditions.
Furthermore, the impact of Persian literature and language, which thrived during the Khilji Dynasty, endured in subsequent periods. Persian continued to be patronized by various rulers, leading to the development of Indo-Persian poetry and a literary culture that persisted for centuries.
Centralized Administration
The administrative reforms introduced by Ala-ud-din Khilji set a precedent for future rulers in India. The emphasis on efficient revenue administration, market control, and delegation of administrative responsibilities influenced subsequent dynasties, contributing to the development of administrative systems that strengthened central authority.
Khilji’s approach to governance and his focus on centralization provided a blueprint for rulers seeking to maintain control over vast empires. The administrative legacy of the Khilji Dynasty shaped the administrative structures of successive dynasties.
In conclusion, the reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji in the Khilji Dynasty had a profound impact on various aspects of India. His military conquests expanded the empire, his administrative reforms centralized authority, and his patronage of arts and culture influenced the social fabric of the subcontinent. The legacy of the Khilji Dynasty, under the rule of Ala-ud-din Khilji, shaped the trajectory of Indian history and left an indelible mark on subsequent dynasties.

Khilji Dynasty in India: Exploring the Reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji
The Khilji Dynasty in India, under the reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji, was a period of significant political and military developments. Ala-ud-din Khilji, who ruled from 1296 to 1316, was known for his bold and ambitious initiatives.
During his reign, Ala-ud-din Khilji expanded his empire through successful military campaigns. He conquered Gujarat, Malwa, and Ranthambore, strengthening the boundaries of his kingdom. He also established a highly efficient administrative system to manage his empire.
One of Khilji’s most notable achievements was his military strategies against the Mongols. He successfully repelled their invasions and even launched counterattacks, showing his strategic brilliance and military prowess.
Ala-ud-din Khilji was also known for his economic reforms. He introduced various policies to control prices and ensure fair taxation, which helped stabilize the economy and improve the living standards of his subjects.
However, his reign was not without controversy. Ala-ud-din Khilji’s treatment of the Rajputs and his efforts to maintain a centralized authority led to conflicts and resistance.
Overall, Ala-ud-din Khilji’s reign marked a crucial period of expansion and consolidation of power for the Khilji Dynasty in India. His military successes and economic reforms shaped the kingdom’s history and legacy.
Key Takeaways
- The Khilji dynasty was one of the most powerful dynasties in India.
- Ala-ud-din Khilji was the most prominent ruler of the Khilji dynasty.
- Ala-ud-din Khilji implemented several reforms to strengthen his rule.
- He introduced the market control system to regulate prices and prevent hoarding.
- Ala-ud-din Khilji was known for his military prowess and successful campaigns.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Khilji Dynasty in India, specifically the reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji, is a fascinating period of Indian history. Here are some frequently asked questions regarding this dynasty and its ruler:1. Who was Ala-ud-din Khilji and what were his major achievements?
Ala-ud-din Khilji was the second ruler of the Khilji Dynasty in India. He ruled from 1296 to 1316 and is known for his military exploits and administrative reforms. His major achievements include:
– Expanding the Khilji Dynasty’s territory through successful military campaigns
– Strengthening the economy through agricultural reforms and trade policies
2. What were Ala-ud-din Khilji’s major military campaigns?
Ala-ud-din Khilji led several successful military campaigns during his reign, expanding the territory of the Khilji Dynasty. Some of his major military campaigns include:
– Conquest of Gujarat in 1299
– Invasion of Ranthambore in 1301
– Capture of Chittorgarh in 1303
3. How did Ala-ud-din Khilji strengthen the economy during his reign?
Ala-ud-din Khilji implemented various economic reforms to strengthen the economy of the Khilji Dynasty. Some of these measures include:
– Introduction of market regulations and price controls
– Encouraging trade and commerce through the construction of roads and canals
– Implementing a system of land revenue assessment
4. What were Ala-ud-din Khilji’s administrative reforms?
Ala-ud-din Khilji introduced significant administrative reforms during his reign to streamline governance. Some of these reforms are:
– Centralizing power and establishing a strong bureaucracy
– Appointing trusted officials to key administrative positions
– Monitoring and auditing the activities of ministers and officials
5. What was Ala-ud-din Khilji’s impact on Indian society and culture?
Ala-ud-din Khilji’s reign had a significant impact on Indian society and culture. Some notable aspects of his influence include:
– Encouraging the promotion of Persian literature and culture
– Implementing stricter social norms and regulations
– Building grand architectural structures, including the Alai Darwaza and the Jama Masjid in Delhi
The Khalji Dynasty || Delhi Sultanate || Medieval History || Lec. 8 || An Aspirant !
In conclusion, the reign of Ala-ud-din Khilji was a significant period in the history of India during the Khilji Dynasty. His rule brought about several important changes and left a lasting impact on the political, military, and economic aspects of the region.
Ala-ud-din Khilji’s military strategies and policies helped expand the empire’s boundaries and strengthened its defense. His administrative reforms, such as the market control system and the introduction of a standardized currency, contributed to the economic growth of the empire.