Ancient China was home to several powerful dynasties that shaped its rich history. Two of the most prominent and influential dynasties were the Han Dynasty and the Tang Dynasty. These dynasties left a lasting impact on Chinese culture, politics, and society, and their contributions continue to influence the world today.
The Han Dynasty, which ruled from 206 BC to 220 AD, is often regarded as a golden age in Chinese history. It was during this time that the concepts of Confucianism and Legalism gained prominence, and significant advancements in technology, arts, and science were made. The Great Wall of China was also expanded during this time to protect the empire from invasions. The Tang Dynasty, on the other hand, thrived from 618 to 907 AD and is considered a time of cultural renaissance. It was known for its prosperous economy, vibrant art and literature, and the spread of Buddhism throughout East Asia.
Ancient China had a long history of several dynasties ruling over the land. Two notable dynasties were the Han Dynasty and the Tang Dynasty. The Han Dynasty, which lasted from 206 BCE to 220 CE, is renowned for its achievements in art, literature, and governance. The Tang Dynasty, spanning from 618 to 907 CE, is known as a golden age in Chinese history, fostering advancements in poetry, music, and trade.
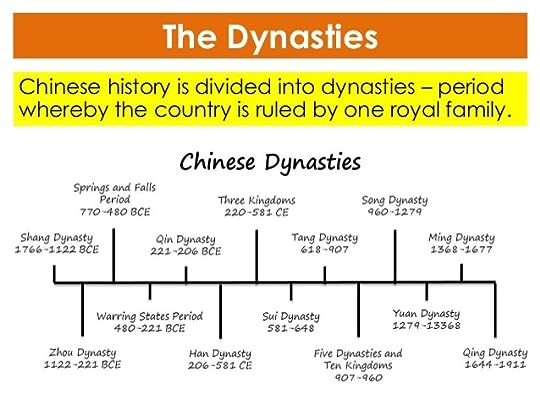
Contents
Introduction to Ancient Chinese Dynasties
Ancient China has a rich and complex history that spans thousands of years, with numerous dynasties ruling over the vast land. As one of the world’s oldest civilizations, these dynasties played a crucial role in shaping China’s culture, politics, economy, and society. In this article, we will explore two of the ancient Chinese dynasties — the Qin Dynasty and the Tang Dynasty.
The Qin Dynasty (221-206 BC)
The Qin Dynasty was the first ruling dynasty to unite China under a centralized imperial rule. It emerged during the Warring States period, a time of intense conflict and chaos among various states. Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of the Qin Dynasty, successfully defeated his rivals and established a strong centralized government.
One of the significant achievements of the Qin Dynasty was the construction of the Great Wall of China. Although much of the wall was rebuilt during later dynasties, the earliest foundations were laid during this period. The Great Wall served as a defensive fortification against invasions from nomadic tribes of the north.
Another notable contribution of the Qin Dynasty was the standardization of various aspects of Chinese society. To create a more cohesive and unified nation, the Qin government standardized measurements, currency, and systems of writing. The creation of a single written script, known as Qin script, laid the foundation for the modern Chinese writing system.
Despite its accomplishments, the Qin Dynasty was marked by a strict and authoritarian rule. The emperor implemented harsh legal codes, centralized political power, and suppressed intellectual dissent. The dynasty’s oppressive policies eventually led to its downfall, as popular uprisings emerged, resulting in the establishment of the next dynasty.
The Tang Dynasty (618-907 AD)
The Tang Dynasty is often considered a golden age in Chinese history due to its significant cultural and economic achievements. It was a time of prosperity and stability, characterized by advancements in art, literature, poetry, and technology. The empire expanded its territory, establishing diplomatic relationships with neighboring countries and facilitating trade along the Silk Road.
During the Tang Dynasty, China witnessed remarkable advancements in science and technology. Inventions such as printing, gunpowder, and the compass had a profound impact not only within the empire but also on the world. These technological breakthroughs played a crucial role in the advancement of knowledge and facilitated the spread of ideas and information.
Another significant development during this period was the flourishing of Chinese poetry. The Tang Dynasty produced many renowned poets, such as Li Bai and Du Fu, whose works are still revered and studied in modern times. Poetry became an integral part of the Chinese cultural tradition and reflected the aspirations, emotions, and societal norms of the time.
The Tang Dynasty was also known for its cosmopolitan nature and international influence. The imperial court welcomed foreign ambassadors, religious missionaries, and scholars from various regions, fostering cultural exchanges and intellectual growth. Buddhism, in particular, gained prominence during this period, with many temples and pagodas constructed across the empire.
Conclusion
The Qin Dynasty and the Tang Dynasty both played crucial roles in the history and development of ancient China. From the unification of China under Qin Shi Huang to the cultural advancements and international influence during the Tang Dynasty, these dynasties left a lasting impact on China and the world. Their legacy continues to shape modern Chinese society and serves as a reminder of the rich and diverse history of this fascinating civilization.

Two Ancient Chinese Dynasties
China’s history is rich with various dynasties that ruled the country for centuries. Two notable ancient Chinese dynasties are the Han Dynasty and the Tang Dynasty.
The Han Dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE) is often referred to as the “Golden Age” of China. It was a period of stability, economic growth, and cultural advancement. The Han Dynasty is known for its administrative reforms, including the establishment of a centralized bureaucracy. The Silk Road, an extensive trade network that connected China with the rest of the world, flourished during this time. The Han Dynasty also witnessed significant advancements in technology, literature, and art, including the invention of paper and the development of classical Chinese poetry.
The Tang Dynasty (618 CE – 907 CE) is regarded as another golden age in Chinese history. It was a period of political stability, economic prosperity, and cultural achievements. The Tang Dynasty is renowned for its impressive military expansion, diplomatic relations with neighboring countries, and the spread of Buddhism. This era witnessed the flourishing of Chinese poetry, painting, and architecture. The capital city of Chang’an (present-day Xi’an) became a vibrant center of art, learning, and commerce. The Tang Dynasty is also known for its advancements in science, medicine, and technology, such as the invention of gunpowder and the printing press.
Key Takeaways – What Are Two of the Ancient Chinese Dynasties
- The Xia Dynasty was the first recorded dynasty in ancient China, known for its legendary ruler, Yu the Great.
- The Shang Dynasty followed the Xia Dynasty and is known for its bronze art, oracle bones, and early Chinese writing.
- Both dynasties played significant roles in shaping China’s culture, government, and social structure.
- The Xia Dynasty laid the foundation for Chinese civilization, while the Shang Dynasty expanded territorial control and developed sophisticated craftsmanship.
- Understanding these ancient dynasties is crucial for comprehending the roots of Chinese history and culture.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we will answer some commonly asked questions about ancient Chinese dynasties.
1. Which two dynasties are considered ancient in Chinese history?
The two ancient Chinese dynasties that hold great significance in Chinese history are:
The Xia Dynasty: The beginning of the Xia Dynasty is believed to be around 2070 BCE, and it lasted for approximately 500 years. Although there is limited archaeological evidence to support its existence, it is considered the first dynasty in Chinese history. The Xia Dynasty is known for its legendary rulers such as Yu the Great, who is credited with controlling floods and developing the agricultural and irrigation systems.
The Shang Dynasty: The Shang Dynasty succeeded the Xia Dynasty and ruled from around 1600 BCE to 1046 BCE. It is the first dynasty for which written records have been discovered. The Shang Dynasty is known for its advanced bronze casting technology, elaborate oracle bone inscriptions, and its hierarchical social structure. The last ruler of the Shang Dynasty was overthrown by Wu Ding, who founded the Zhou Dynasty.
2. What were some notable achievements of the Xia Dynasty?
The Xia Dynasty, despite limited evidence, is attributed with several notable achievements:
1. Development of Agriculture and Irrigation: The Xia Dynasty focused on improving agricultural practices and developing irrigation systems. This led to increased food production, which in turn supported a growing population.
2. Control of Floods: Yu the Great, a legendary ruler of the Xia Dynasty, is known for his success in controlling floods and redirecting waterways. His efforts helped prevent floods and effectively manage rivers, benefiting the agricultural communities.
3. What were the major contributions of the Shang Dynasty?
The Shang Dynasty made significant contributions that shaped ancient Chinese civilization:
1. Bronze Casting: The Shang Dynasty revolutionized the art of bronze casting, creating intricate bronze vessels for rituals and ceremonies. These vessels showcased the technological advancements and artistic skills of the time.
2. Oracle Bone Inscriptions: The Shang Dynasty developed a system of divination using oracle bones, which were inscribed with questions and predictions. These inscriptions provide valuable insights into the ancient Shang society, including their religious beliefs and social structure.
4. How did the Xia Dynasty come to an end?
The downfall of the Xia Dynasty is shrouded in legend and historical uncertainty. According to ancient texts, the last ruler, Jie, was known for his tyrannical and oppressive rule. This prompted a rebellion led by Tang, who founded the Shang Dynasty. The exact details of this event are still debated among historians and archaeologists.
5. What led to the decline of the Shang Dynasty?
The Shang Dynasty faced several challenges that contributed to its decline:
1. Internal Conflicts: Towards the later period of the Shang Dynasty, there were internal power struggles and conflicts within the ruling elite. This weakened the central authority of the dynasty and created divisions within the society.
2. External Invasions: The Shang Dynasty faced invasions from neighboring tribes, particularly the Zhou people. The Zhou Dynasty ultimately overthrew the Shang Dynasty, marking the end of its rule. The Zhou Dynasty went on to establish its own ruling dynasty, known as the Western Zhou.
History Of Ancient China | Dynasties, Confucius, And The First Emperor
In summary, two of the ancient Chinese dynasties were the Qin Dynasty and the Han Dynasty. The Qin Dynasty, founded in 221 BCE by Qin Shi Huang, was known for its centralized rule and the construction of the Great Wall of China. It was a short-lived dynasty but left a significant impact on Chinese history.
The Han Dynasty, which followed the Qin Dynasty, lasted for over four centuries and is regarded as a golden age in Chinese history. This dynasty saw advancements in various fields, including governance, arts, and technology. The Han Dynasty also played a crucial role in the spread of Confucianism as the state ideology.